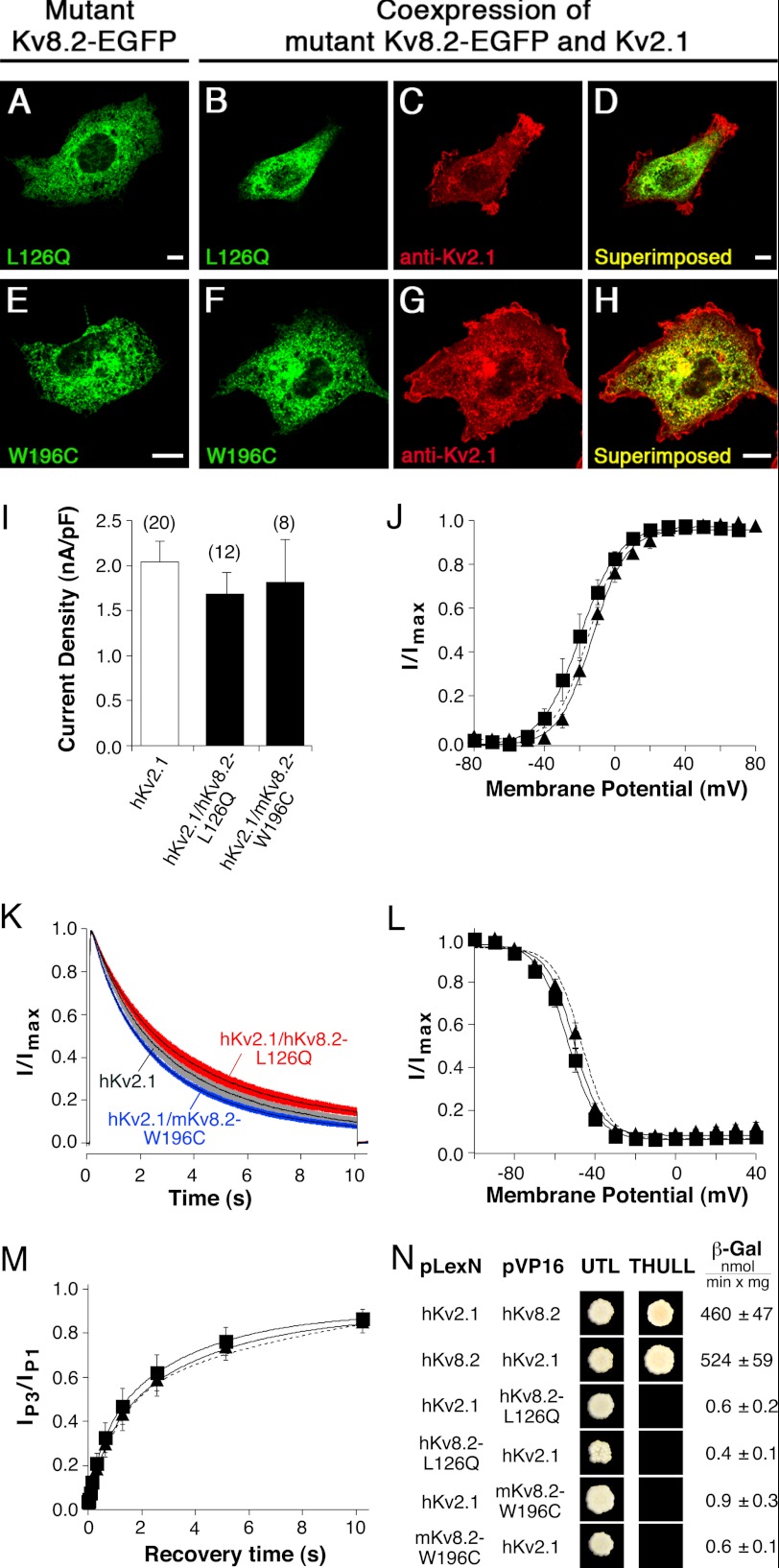
FIGURE 5.
Characterization of missense mutations located in the NH2 terminus of Kv8.2 (hKv8.2-L126Q and mKv8.2-W196C). Mutant α-subunits were expressed alone or together with the Kv2.1 α-subunit in COS7L cells in a 1:3 ratio. Confocal pictures show the following. A, hKv8.2-L126Q-EGFP; B and C, coexpression of hKv8.2-L126Q-EGFP with hKv2.1; D, superimposition of B and C; E, mKv8.2-W196C-EGFP; F and G, coexpression of mKv8.2-W196C-EGFP with mKv2.1; H, superimposition of F and G. Green fluorescence indicates mutant Kv8.2-EGFP subunits; red fluorescence indicates Kv2.1 α-subunits. Scale bars, 10 μm. I, bar diagram summarizing the current densities observed in HEK 293 cells expressing the indicated α-subunits: hKv2.1 (2.04 ± 0.24 nA/pF, n = 20), hKv2.1/hKv8.2-L126Q (1.68 ± 0.24 nA/pF, n = 12), and hKv2.1/mKv8.2-W196C (1.81 ± 0.48 nA/pF, n = 8). J, voltage dependence of activation on coexpression of hKv2.1 with hKv8.2-L126Q (■) and hKv2.1 with mKv8.2-W196C (▴). The dashed line corresponds to the voltage dependence of activation observed for hKv2.1 (Fig. 2C). K, comparison of the inactivation from the open state on coexpression of hKv2.1 with hKv8.2-L126Q (red), hKv2.1 with mKv8.2-W196C (blue), or expression of hKv2.1 (gray). Currents were elicited by a 10-s voltage step to +30 mV. Solid lines represent mean currents with shading indicating the S.E. L, voltage dependence of the steady-state inactivation. For the coexpression of hKv2.1 with hKv8.2-L126Q (■) and for hKv2.1 with hKv8.2-W196C (▴), channels were inactivated for 20 s at prepulse potentials ranging from −100 mV to +40 mV, followed by a test pulse to +60 mV to activate residual noninactivated channels. The Boltzmann curve obtained for hKv2.1 (Fig. 2F) is shown for comparison (dashed line). M, time dependence of the recovery from inactivation for the coexpressions of hKv2.1 with hKv8.2-L126Q (■) and hKv2.1 with mKv8.2-W196C (▴). The pulse protocol was identical to that described in Fig. 2H for the homomeric hKv2.1 channel. The exponential fit obtained for the recovery of hKv2.1 (from Fig. 2H) is shown for comparison (dashed line). N, yeast two-hybrid assay probing the homo- and heteromeric interactions mediated by the indicated NH2 termini. Growth observed after pairwise transformation of yeast two-hybrid constructs pLexN-KvX.Y and pVP16-KvX.Y (indicated on the left) on UTL− medium indicates successful transformation and growth on THULL− medium indicates interaction of fusion proteins. The last column shows the mean values obtained for the semi-quantitative test of interaction using the β-gal reporter gene.