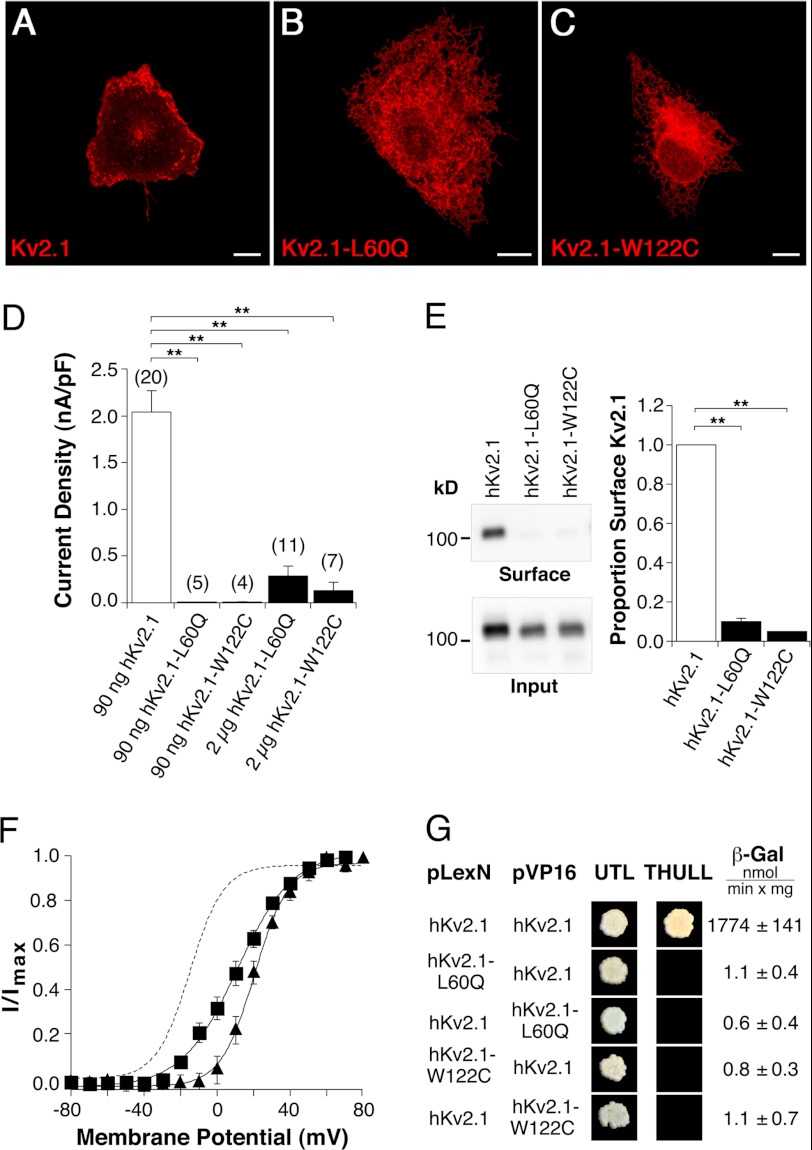
FIGURE 6.
Functional consequences of amino-terminal missense mutations on hKv2.1 channel characteristics. hKv2.1-L60Q corresponds to hKv8.2-L126Q, and hKv2.1-W122C corresponds to hKv8.2-W188C. Confocal pictures show the following expression: A, hKv2.1; B, hKv2.1-L60Q; and C, hKv2.1-W122C in COS7L cells. Red fluorescence indicates hKv2.1 α-subunits. Scale bars, 10 μm. D, bar diagram summarizing the current densities observed in HEK293 cells expressing the indicated α-subunits. E, immunoblot revealing the surface expression of hKv2.1, hKv2.1-L60Q, and hKv2.1-W122C in COS7L cells. Bar diagram showing the proportion of hKv2.1-L60Q (n = 3) and hKv2.1-W122C (n = 3) that reach the plasma membrane with respect to hKv2.1. F, voltage dependence of activation of hKv2.1-L60Q (■) and hKv2.1-W122C (▴) channels. The dashed line corresponds to the voltage dependence of activation observed for hKv2.1 (Fig. 2C). G, results of the yeast two-hybrid assay. Growth observed after pairwise transformation of yeast two-hybrid constructs pLexN-KvX.Y and pVP16-KvX.Y (indicated on the left) on UTL− medium indicates successful transformation, and growth on THULL− medium indicates interaction of the fusion proteins. The last column shows the mean values obtained for the semiquantitative test of interaction using the β-gal reporter gene.