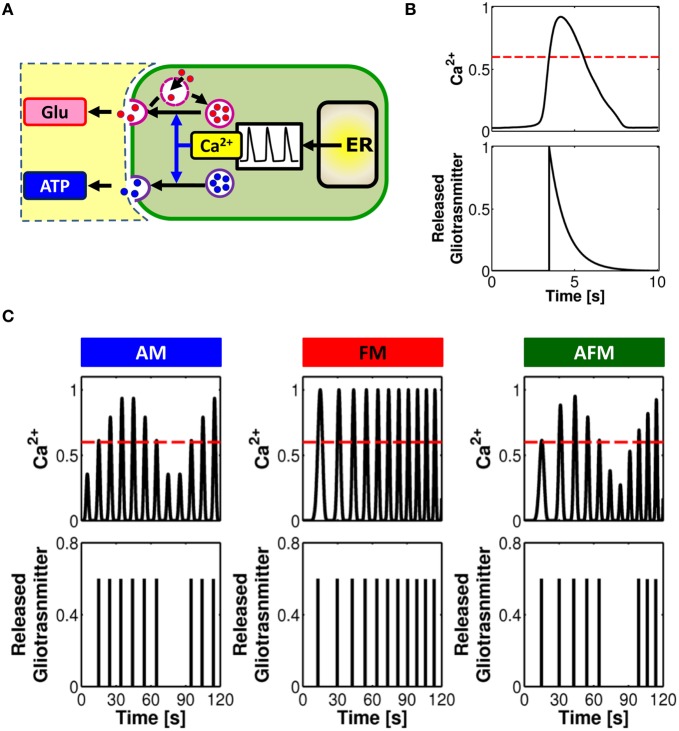
Figure 3.
Linking gliotransmitter exocytosis to various Ca2+ encoding modes. (A) Calcium-dependent glutamate and ATP exocytosis from astrocytes are both brought forth by a vesicular compartment in the astrocyte competent for regulated exocytosis. The frequency of exocytotic events is directly controlled by the shape and frequency of Ca2+ oscillations. (B) Modeling concept for an “exocytosis event” from the astrocyte. Calcium (top trace) triggers exocytosis of glutamate or ATP every time it increases beyond a certain threshold concentration value (red dashed line). The overall release can then be approximated, under proper assumptions, by an exponentially-decaying pulse of extracellular concentration of glutamate or ATP (bottom trace). (C) Distinct Ca2+ encoding patterns could translate into distinct rates of gliotransmitter exocytosis events. In this way, synaptic activity encoded by astrocytic Ca2+ signals is linked to the frequency of glutamate/ATP release from the astrocyte in a unique fashion. Adapted from De Pittà et al. (2011).