Figure 2.
GlyCl-mediated depolarization induces abnormal vascular structure in vivo.
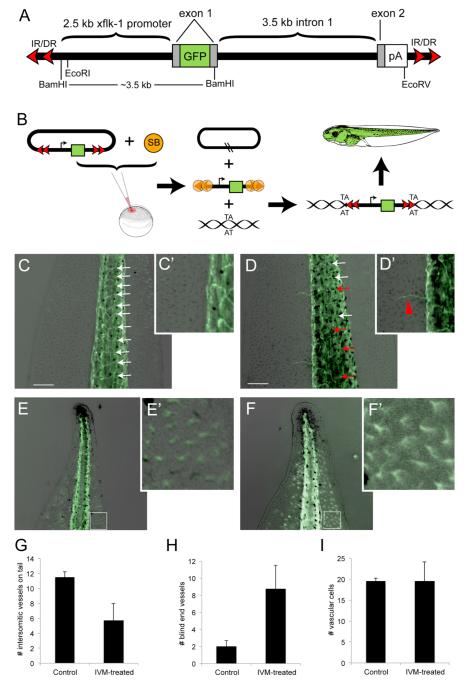
(A) Schematic of the pT2xflk-1:GFP transposon gene, adapted from (Doherty et al., 2007) and not drawn to scale. The green fluorescent protein (GFP) on exon 1 is driven by a flk-1 promoter 2.5 kb upstream. A polyadenylation signal (pA) was cloned to maintain the integrity of the splice acceptor. The xflk-1:GFP construct was cloned into the pT2 non-autonomous transposon between the invert-direct repeats (IR/DR). (B) Mechanism of SB-mediated transposition. The pT2flk-1:GFP was injected together with Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase mRNA into fertilized eggs at the one-cell stage. SB transposase binds to the IR/DRs as shown and cuts the transposon (containing the flk-1 promoter driving GFP expression) out of the plasmid (the cut sites are indicated by the two black slashed lines in the remaining plasmid). A DNA molecule with a ‘TA’ sequence becomes the recipient of a transposed transposon; transgenic animals bearing this fluorescent marker of vasculature were used in experiments where instructor cells were depolarized with ivermectin.
(C, C’) In untreated pT2flk-1:GFP Xenopus laevis transgenic tadpoles, the intersomitic vessels on the tail are evenly spaced (white arrows) and tail regions largely lack blind end vessels. (D, D’) Ivermectin-treated embryos display an overall decrease the number of intersomitic vessels (G), as well as an increase in disrupted intersomitic vessels (red arrows), and an increase in the amount of small blind-end vessels extending into the tail fin region (H). To determine whether there was an increase in vascular cells in the tail tip between control and ivermectin-treated embryos (E,F), the number of GFP-positive cells in a 200 μm square region (white boxes) was counted. While there is no difference in the number of vascular cells in the tail tip between treatments (I), the shape of the vascular cells in ivermectin-treated embryos (F’) compared to controls (E’) reveals an increase in arborization. Scale bars, 250 μm.