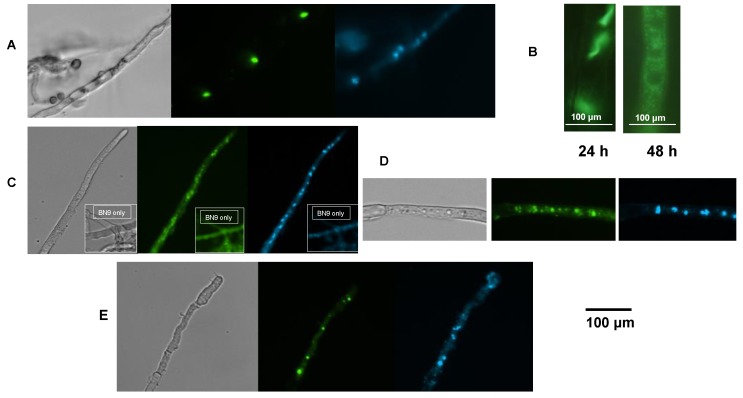
Figure 5.
AflJ and AflR localization in A. parasiticus of GFP- and eYFP-tagged fusion proteins. (A) AflJ::GFP localization: expression of the fusion construct was under the control of the gpdA promoter. Mycelia were obtained from cultures of transformants of A. parasiticus ΔaflJ with pPTRI-gpdA-GFP::aflJ-trpC grown on PDB medium for 24 h. The mycelia was stained with DAPI and examined for fluorescence using a GFP and a DAPI filter; (B) AflJ::GFP localization when the fungi were grown on YES medium for 24 and 48 h; (C) AflJ::GFP localization when expression of the fusion protein was under control of the aflJ promoter. Fluorescence was determined on A. parasiticus mycelia when the fungus was transformed with pPTRI-aflJ promoter-GFP::aflJ-trpC terminator grown on PDB for 18 h. Insets show self-fluorescence and DAPI-fluorescence when the wild-type A. parasiticus BN9 was examined in the microscope under the same conditions; (D) AflR::GFP localization. Fluorescence was determined on A. parasiticus transformed with gpdA-YFP::aflR-trpC grown as above; (E) AflJ and AflR split YFP (BiFC) studies. Fluorescence was determined on mycelia obtained from A. flavus co-transformed with plasmids amyB-aflR::Nt-YFP and amyB-aflJ::Ct-YFP. All micrographs were acquired at 400× final magnification.