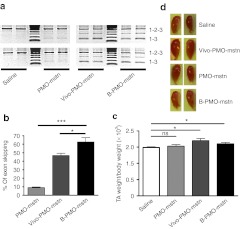
Figure 2.
Single intramuscular injection of PMO-mstn linked to an arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide in C57BL10 mice increases muscle mass. Tibialis anterior (TA) muscles of C57BL10 mice were treated with 10 µg of unconjugated PMO-mstn, Vivo-PMO-mstn, B-PMO-mstn or excipient (n = 6). Mice were killed after 8 weeks and nested RT-PCR was performed on treated and control muscle RNAs. (a) Representative products of nested RT-PCR analysis of myostatin exon 2 skipping from muscles treated with the different PMOs are shown. (b) Densitometric analyses of nested RT-PCR products for percentage of myostatin exon 2 skipping in treated and control muscles. A statistically significant difference was observed in exon skipping mediated by B-PMO-mstn compared with both Vivo-PMO-mstn and unconjugated PMO (*P = 0.02 and ***P < 0.0001 respectively, two-tailed t-test, n = 6). Both bands corresponding to skipped products were included in the analysis. (c) Change of mass in treated and control muscles. Both B-PMO-mstn (P = 0.04) and Vivo-PMO-mstn (P = 0.01) treated muscles were significantly heavier than control muscles (two tailed t-test, *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, n = 6). (d) Representative TA muscles collected 8 weeks after treatment with the different PMOs or with excipient. ns, not significant; PMO, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR.