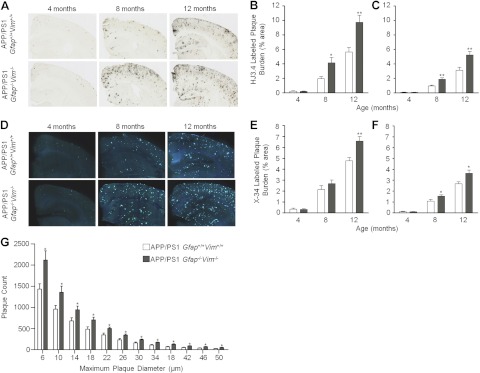
Figure 1.
Deletion of Gfap and Vim accelerates amyloid plaque pathogenesis. A–F) Brain sections from APP/PS1 Gfap+/+Vim+/+ and APP/PS1 Gfap−/−Vim−/− mice were immunostained with anti-Aβ antibodies (A) or stained with X-34 to label plaques (D). Gfap and Vim deletion increased Aβ-immunostained plaque load in the cerebral cortex (B) and hippocampus (C) at 8 and 12 mo of age, but there was no difference at 4 mo in either region. X-34-stained “compact” plaque load was also increased in cerebral cortex (E) and hippocampus (F) in APP/PS1 Gfap−/−Vim−/− mice. G) Size-frequency histogram of X-34-labeled amyloid plaques in 12-mo-old APP/PS1 Gfap+/+Vim+/+ (open bars) and APP/PS1 Gfap−/−Vim−/− (shaded bars) mice. APP/PS1 Gfap−/−Vim−/− mice had more plaques in every size category. Values are expressed as means ± se; n = 8–11 mice/group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.