Figure 1.
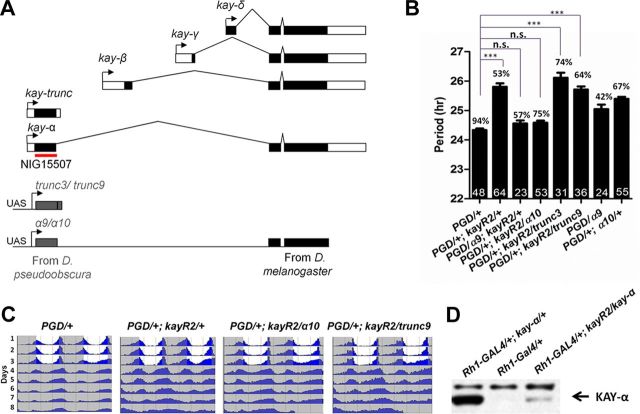
Downregulating kay-α lengthens the period of free-running circadian behavior in DD. A, Organization of the kay locus in D. melanogaster. kay is predicted to produce five isoforms. The dark boxes indicate coding sequences, and open boxes indicate noncoding sequences. Transgene NIG15507 generates dsRNAs targeting both the α and trunc isoforms. The red line indicates the region targeted by dsRNA. Constructs for cross-species rescue experiments are shown on the bottom of the panel. α9, α10, trunc3, and trunc9 are insertions of UAS-controlled transgenes that generate kay mRNAs resistant to the NIG15507 dsRNAs. The region targeted by NIG15507 dsRNAs was replaced with homologous D. pseudoobscura sequences. B, Downregulation of kay-α lengthens circadian behavior period. Bars 1 and 2, Flies expressing dsRNAs targeting kay-α and kay–trunc under the Pdf–GAL4 driver have ∼26-h-long period rhythms (control, 24.4 h). PGD: Pdf-GAL4, UAS-dcr2. Bars 3–6, The kay RNAi phenotype can be rescued with the kay-α construct resistant to the dsRNAs but not with the kay–trunc construct. Bars 7 and 8, The rescue is not explained by a period shortening caused by expression of the chimeric kay-α, because its expression in wild-type flies does not shorten circadian behavioral rhythms (it actually slightly lengthens them). Error bars correspond to SEM. Digits in the bar are the numbers of tested flies. Percentage of rhythmicity is indicated above the bars. One-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001. Tukey's multiple comparison test. ***p < 0.001; n.s., not significant at level of 0.05. C, Double-plotted actograms showing the average activity for each genotype. Flies were entrained in standard LD cycle for 3 d and then released in DD. D, The NIG15507-R2 transgene can inhibit KAY-α expression in vivo. Fly head extracts were immunoblotted with an anti-KAY-α/TRUNC antibody. Strong immunoreactivity was observed when KAY-α was misexpressed in the eyes with the Rh1–GAL4 driver (lane 1), whereas endogenous KAY-α was undetectable (lane 2). dsRNAs generated by NIG15507-R2 transgene were able to dramatically knock down the overexpression of KAY-α (lane 3).