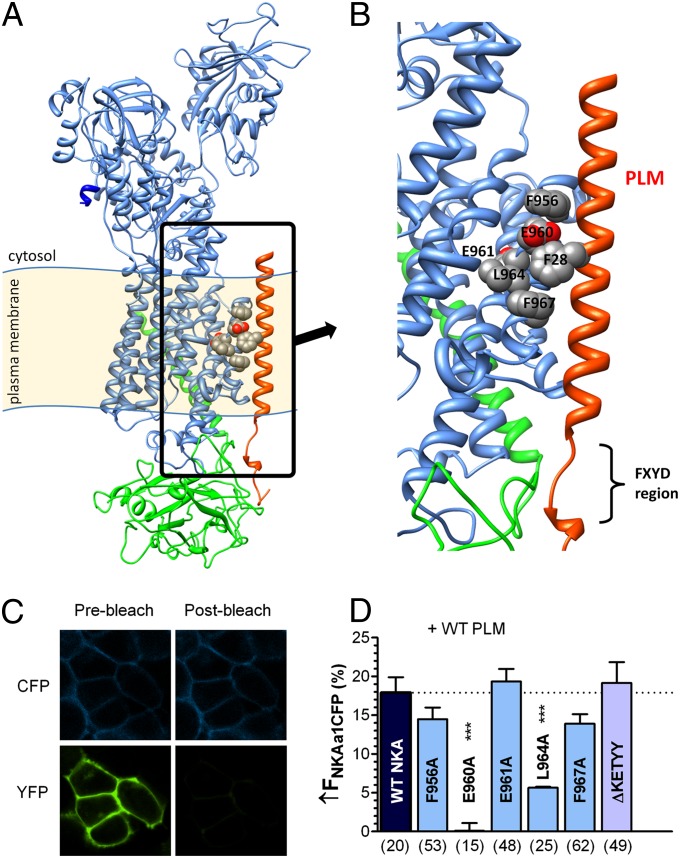
Fig. 1.
E960 site on NKA is critical for NKA–PLM FRET. (A) Structural model of rat NKA α-subunit (blue), β-subunit (green), and PLM (red). Putative PLM interaction sites on NKA TM9 are highlighted. (B) Magnified picture of highlighted area in Fig. 1A showing putative PLM interaction sites on NKA TM9: F956, E960, E961, L964, and F967. (C) HEK293 cells coexpressing CFP–NKA-α1 and PLM–YFP before and after photobleaching YFP. FRET was measured as the increase in donor (CFP) fluorescence upon acceptor photobleaching. (D) Average FRET (±SEM) between CFP–NKA-α1 and PLM–YFP with indicated NKA mutations (n below the bars, ***P < 0.0001, statistical significance vs. WT–NKA using unpaired t test.