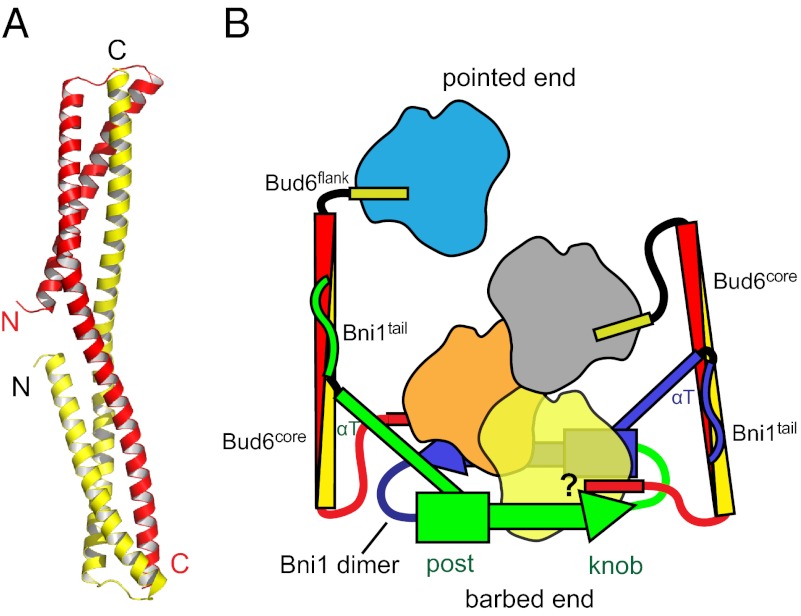
Fig. P1.
Structure of the Bud6core domain and a model for actin filament nucleation by the Bni1/Bud6 complex. (A) Ribbon diagram of the Bud6core domain, with the N- and C-terminal ends of the fragment labeled and with one chain of the dimer colored red and the other yellow. (B) Working model for actin nucleation on Bni1, derived from the work described here and from structures of the Bni1 FH2 domain alone and with actin (5). The two sides of the formin dimer are shown in green and blue, and the actin subunits are shown in yellow, orange, gray, and blue. The Bni1 FH2 dimer binds two Bud6 dimers, and Bud6, in turn, may bring a total of four actin subunits into the nascent filament. After the nucleus is formed, Bud6 may remain associated or dissociate from Bni1 as actin elongation proceeds, with the formin processively tracking the barbed end of the growing filament. As indicated by the question mark, it is unclear whether Bud6 and Bni1 can simultaneously engage the same actin subunit.