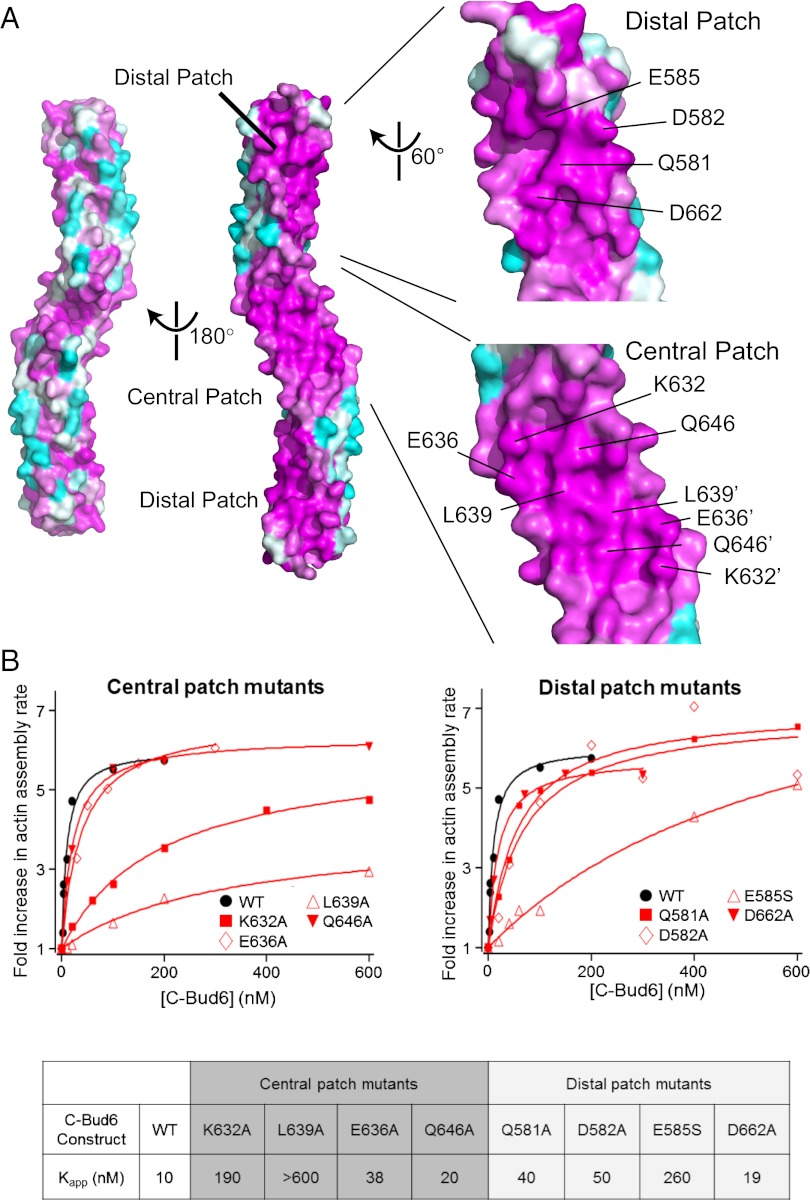
Fig. 3.
Identification of conserved functional surface residues on Bud6core. (A) Surface conservation of Bud6core. Each residue is labeled with a color ranging from the most conserved (magenta) to the most variable (cyan) as analyzed with ConSurf (37). The eight residues that were mutated for biochemical analysis are indicated on the surface in the zoomed-in view. The two identical central patches are contiguous; residues contributing to these patches are distinguished by the use of prime symbols in their labels. (B) Concentration-dependent effects of WT and mutant c-Bud6 polypeptides on Bni1-mediated actin assembly. Monomeric actin (2 μM, 2.5% pyrene-labeled) was polymerized in the presence of 10 nM Bni1 (FH1-FH2-C) and variable concentrations of c-Bud6 as indicated. Each data point is an average of at least two trials in which the maximum rate of actin assembly over the course of the reaction was determined. All values were normalized to the rate of actin assembly occurring in the presence of 10 nM Bni1 alone. The Kapp value for each mutant was calculated by determining the concentration of mutant c-Bud6 required to increase the rate of Bni1-mediated assembly to half of the maximal rate observed for WT c-Bud6.