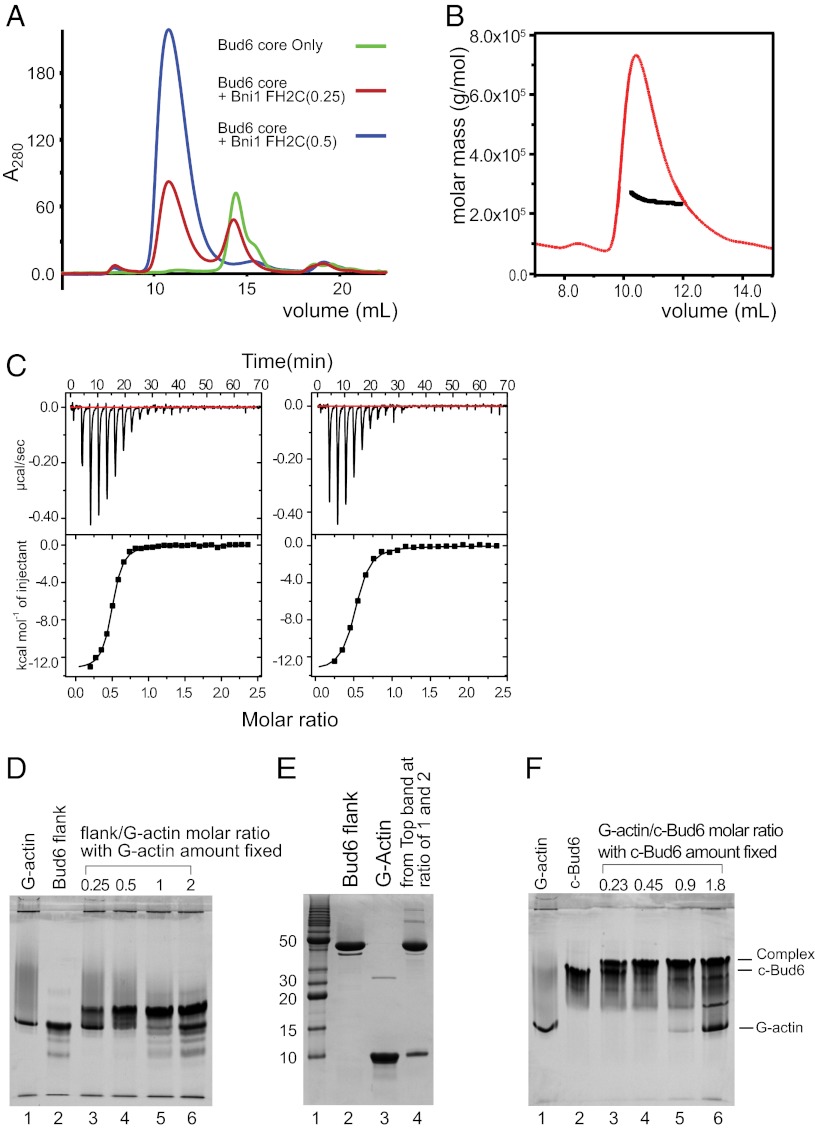
Fig. 6.
Stoichiometry of Bud6 interaction with Bni1 and G-actin. (A) Analysis of Bni1-FH2C/Bud6core mixtures by SEC. Bud6core alone, or with addition of a 0.25 or 0.5 molar ratio of Bni1-FH2C as indicated, was analyzed by SEC on a Superdex 200 column. Note that a 0.5 ratio of Bni1-FH2C was sufficient to ablate the free Bud6core peak (blue trace). Quantitation of Bud6core and Bni1-FH2C in the peak eluting at ∼11 mL by densitometry of the elution fractions resolved by SDS/PAGE confirmed a 2:1 ratio of Bud6core to Bni1-FH2C. (B) SEC-MALS analysis of c-Bud6/Bni1-FH2C indicated a molar mass of ∼240 kDa. Molar mass (black) and refractive index (red) are plotted vs. elution volume from a Superdex 200 size-exclusion column. A 2:1 complex of c-Bud6/Bni1 dimers has an expected mass of ∼250 kDa. (C) Analysis of Bud6 binding to Bni1tail by ITC. (Left) Titration of Bud6core with Bni1tail yielded a stoichiometry of n = 0.48 and Kd = 0.75 μM. (Right) Titration of c-Bud6 with Bni1tail produced similar results (n = 0.49 and Kd = 1.1 μM). (D) Native-PAGE analysis indicating that Bud6flank forms a 1:1 complex with G-actin. The amount of G-actin was fixed, and the amount of Bud6flank was gradually increased by the molar ratio indicated. (E) SDS/PAGE analysis of bands from a Bud6flank/G-actin native-PAGE gel shift assay. The upper bands from Bud6flank/G-actin molar ratios of 1 and 2 in D were excised, combined, and resolved on a 20% SDS/PAGE denaturing gel. (F) Native-PAGE analysis indicates that c-Bud6 forms a 1:1 complex with G-actin. A fixed amount of c-Bud6 was combined with an increasing molar ratio of G-actin as indicated and analyzed on 20% native gel. All protein concentrations were determined by amino acid analysis.