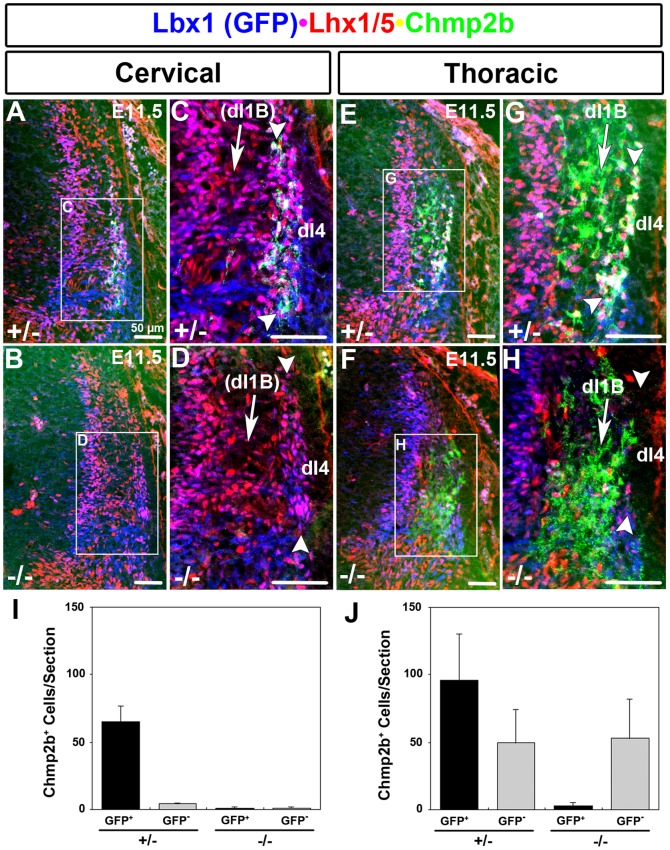
Figure 6. Lbx1-Independent Domain Absent at Cervical Levels.
(A–D) Dorsolateral neural tube at cervical levels. A lateral column (bracketed by arrowheads) shows cells that are colabeled by Lbx1(GFP) and Lhx1/5. A subset of these cells are also labeled by Chmp2b in heterozygotes but not in mutants. The size of the lateral column is also reduced, possibly reflecting the loss of dI4 cells, as observed at thoracic levels. The Lbx1-independent expression domain in the circumferential trajectory, representing dI1B cells, is absent in both genotypes. (E–H). Dorsolateral neural tube at thoracic levels. A lateral column (bracketed by arrowheads) shows dI4 cells that are colabeled by Lbx1(GFP) and Lhx1/5. Almost all of the cells in this column are labeled by Chmp2b in heterozygotes. The column is absent in mutants. A large Lbx1-independent expression domain in the circumferential trajectory, representing dI1B cells, is present in both genotypes. It is adjacent to the dI4 column and obscured the loss of Chmp2b RNA in the dI4 column at thoracic levels (see results). (I, J) Quantification of cells in GFP/Lhx1/5/Chmp2b labeled heterozygote sections at cervical (n = 4) and thoracic (n = 4) levels, respectively. Primary antibodies against GFP, Lhx1/5, and Chmp2b were detected using appropriate Cy2 (green), Cy3 (red), and Cy5 (infrared)secondary antibodies, respectively. Colors were electronically switched, for clarity, to those indicated by the labels.