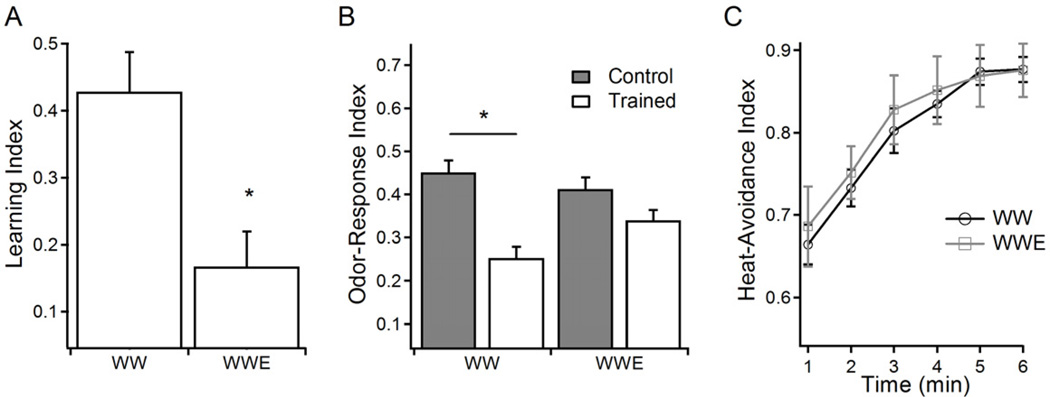
Figure 2. Acute ethanol treatment impairs learning.
A) Larvae fed ethanol food for 1 hour (WWE) showed reduced learning when compared to ethanol-naive larvae (WW). (* p=0.006, N=7). B) Shown are odor-response indices for the water-treated (WW) and acutely treated ethanol group (WWE). Gray bars are mock-trained and open bars are trained larvae. There was an overall significant effect of training (* p<0.001), however posttests indicated that trained and control responses differed only within WW group but not within WWE group (* p<0.001 for WW p>0.05 for WWE, N=8). C) The ethanol treatment did not alter larval sensitivity to heat as both groups avoided the heated section of a dish at the same rate. There was a significant effect of time during the test (* p<0.0001), but not of treatment (p=0.7514). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).