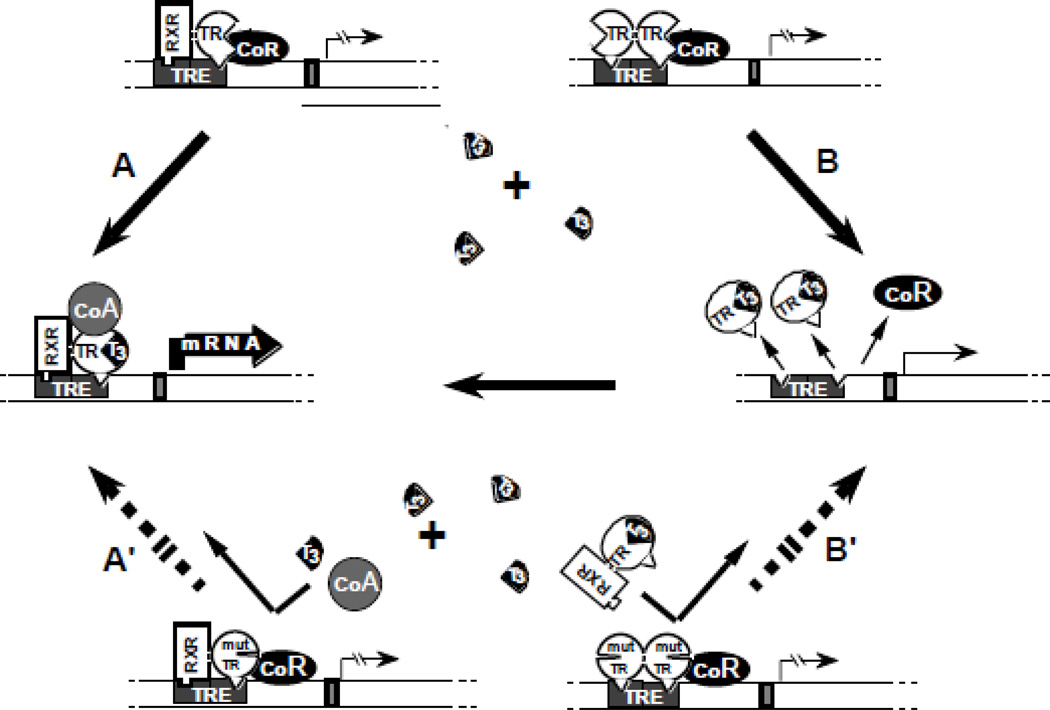
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the DNE mechanism: In the absence of T3, occupancy of TRE by TR heterodimers (TR-RXR) or dimers (TR-TR) suppresses transactivation through association with a corepressor (CoR). (A) T3-activated transcription mediated by TR-RXR heterodimers involves the release of the CoR and association with coactivators (CoA) as well as (B) the removal of TR dimers from TRE releases their silencing effect and liberates TREs for the binding of active TR-RXR heterodimers. The DNE of a mutant TR (mut TR), that does not bind T3, can be explained by the inhibitory effect of mut TR-containing-dimers and heterodimers that occupy TRE. Thus, T3 is unable to activate the mut TR-RXR heterodimer (A') or release TREs from the inactive mut TR homodimers (B'). (Modified from Refetoff S, Weiss RE, Usala SJ. The syndromes of resistance to thyroid hormone. Endocr Rev 1993;14:348–399.)