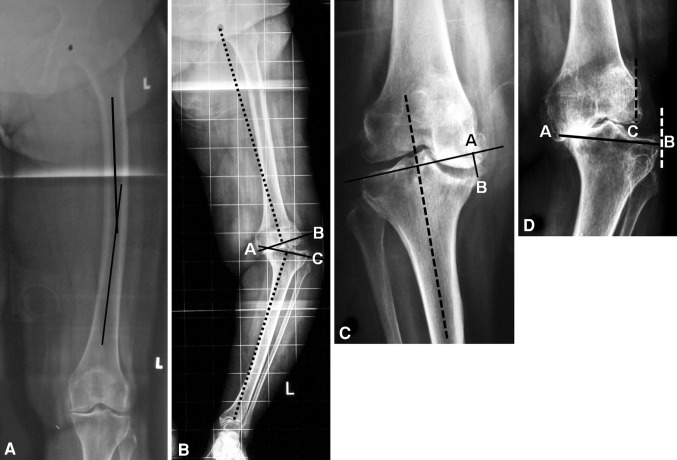
Fig. 1A–D.
(A) Femoral bowing in the coronal plane is measured on a full-length hip-to-ankle radiograph as the angle made by the middiaphyseal lines of the proximal ½ and distal ½ of the femoral shaft. (B) JDA (Angle BAC) is measured as the angle made by the distal femur and proximal tibial cuts (solid lines) plotted perpendicular to the femoral and tibial mechanical axes (dotted lines). (C) Depth of tibial bone loss (Distance AB) is measured on standing knee AP radiographs as the distance between the tangential line (solid line) drawn to the top of the intact lateral tibial plateau perpendicular to the proximal tibial mechanical axis (dotted line) and the lowest point of the defect. (D) Amount of tibial subluxation is measured as a percentage of the distance between the lateral-most point of the distal femoral condyle to the lateral-most point of the tibial condyle (Distance CB) with respect to the mediolateral length of the tibial plateau at the level of the articular surface (Distance AB), ie, amount of tibial subluxation = Distance CB × 100/Distance AB.