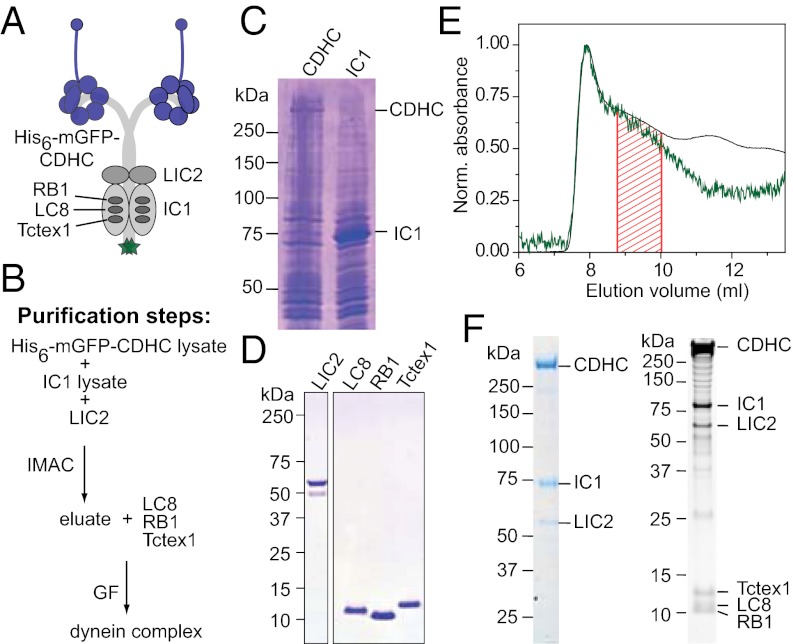
Fig. 1.
Reconstitution of the human cytoplasmic dynein complex. (A) Schematic of the subunit composition of the dynein complex studied here. A His6 tag, followed by mGFP (green), is fused to the N terminus of the CDHC (Fig. S1A, Top). (B) Purification scheme: lysates of cells expressing His6-mGFP-CDHC (C, lane 1; 560 kDa; referred to here as CDHC) and cells expressing IC1 (C, lane 2; 71 kDa) were mixed, supplemented with purified LIC2 (D, lane 1; 54 kDa), and subjected to immobilized metal-ion–affinity chromatography (IMAC). The eluate was supplemented with purified light chains (D, lanes 2–4; 10–13 kDa) and gel-filtered (GF). (C and D) Coomassie-stained SDS gels showing lysates of cells expressing CDHC and IC1 (C) and purified LIC2 and light chains (D), as indicated. (E) Gel-filtration profile around the position where the dynein complex elutes showing normalized absorbance values at 280 nm (black line) and 488 nm (green line). The fraction between the red lines was collected and analyzed. (F) Coomassie-stained (Left) and SYPRO Ruby–stained (Right) SDS gel showing the dynein complex after gel filtration.