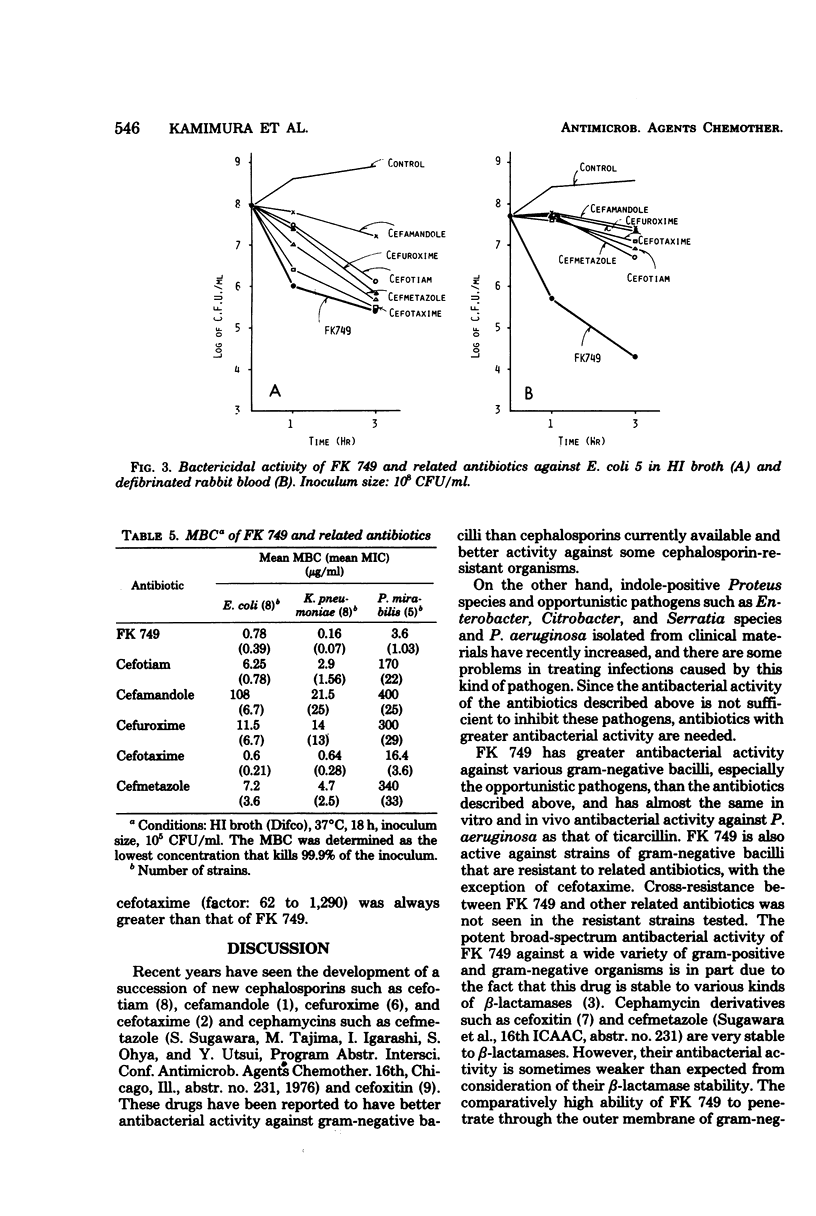
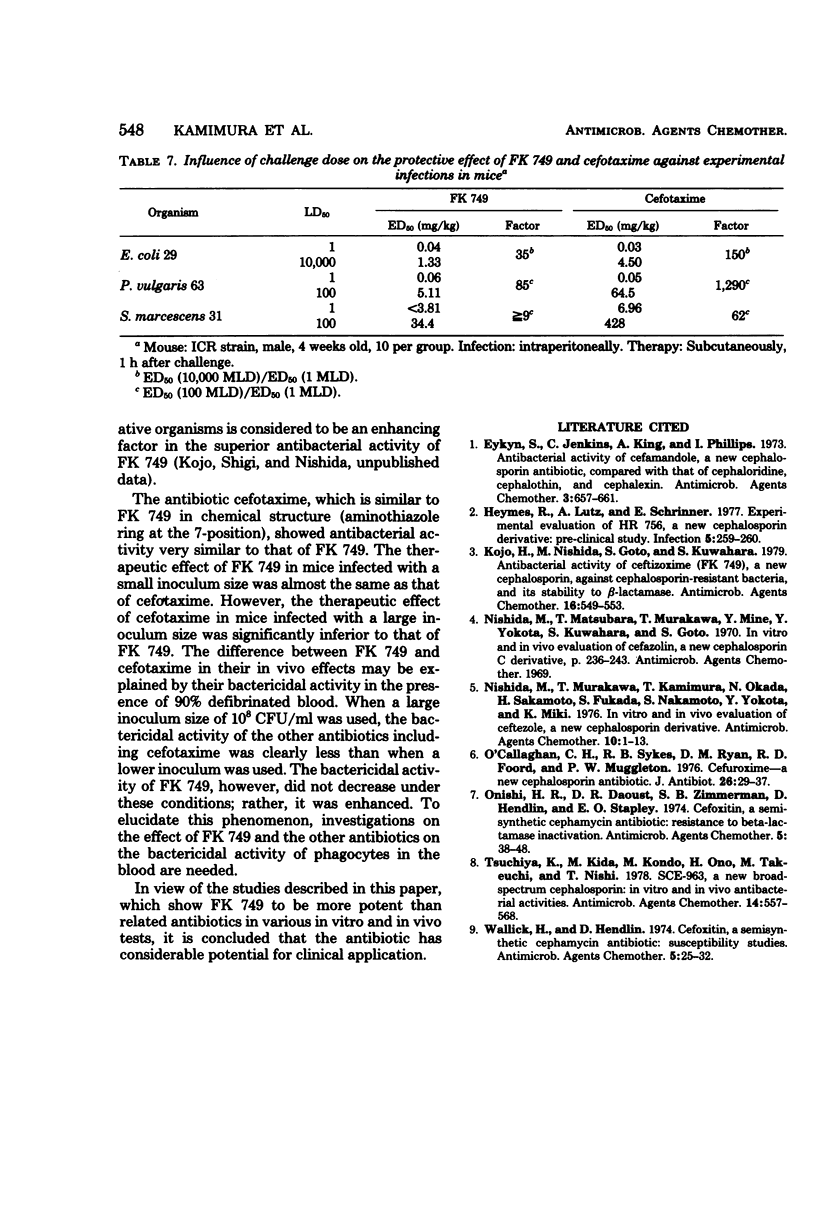
Abstract
FK 749 is a new parenteral cephalosporin derivative which is more active against various gram-negative bacilli, including the opportunistic pathogens such as Enterobacter, Citrobacter species, and Serratia marcescens, than cephalosporins and cephamycins such as cefotiam, cefamandole, cefuroxime, cefotaxime, and cefmetazole. FK 749 was especially active against gram-negative organisms resistant to these related antibiotics. FK 749 was more potent in bactericidal activity than the other antibiotics, and the activity was clearly enhanced in the presence of 90% defibrinated rabbit blood. The therapeutic effect of subcutaneously injected FK 749 in mice infected with various gram-negative bacilli was far superior to that of cefotiam, cefamandole, cefuroxime, and cefmetazole and was almost the same as that of cefmetazole in mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus and that of ticarcillin in mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FK 749 has, in general, nearly the same in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities as cefotaxime. The former had more potent bactericidal activity in the presence of the blood than the latter and showed more excellent therapeutic effect than cefotaxime against infections caused by large inoculum sizes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefamandole, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):657–661. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymès R., Lutz A., Schrinner E. Experimental evaluation of HR756, a new cephalosporin derivative: pre-clinical study. Infection. 1977;5(4):259–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01640793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojo H., Nishida M., Goto S., Kuwahara S. Antibacterial activity of ceftizoxime (FK 749), a new cephalosporin, against cephalosporin-resistant bacteria, and its stability to beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Murakawa T., Kamimura T., Okada N., Sakamoto H., Fukada S., Nakamoto S., Yokota Y., Miki K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ceftezole, a new cephalosporin derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Ryan D. M., Foord R. D., Muggleton P. W. Cefuroxime - a new cephalosporin antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jan;29(1):29–37. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Daoust D. R., Zimmerman S. B., Hendlin D., Stapley E. O. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: resistance to beta-lactamase inactivation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kida M., Kondo M., Ono H., Takeuchi M., Nishi T. SCE-963, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):557–568. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Hendlin D. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: susceptibility studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



