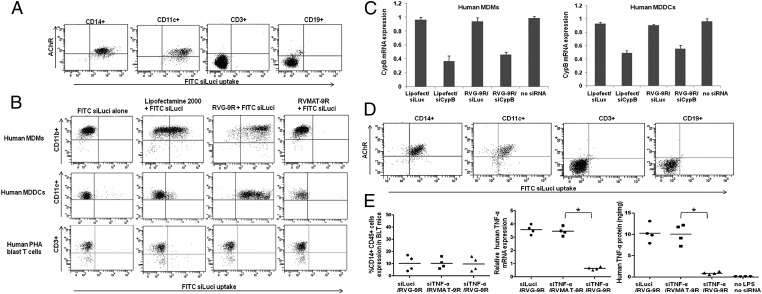
Fig. 2.
RVG-9R delivers siRNA to primary human macrophages and DCs. (A) Ex vivo–isolated human PBMCs were incubated with FITC siLuci complexed with RVG-9R for 4 h before staining with antibodies to AchR, CD14, CD11c, CD3, and CD19. CD14-, CD11c-, CD3-, and CD19-gated cell populations were examined for FITC uptake by flow cytometry. The experiment was repeated two times with similar results. (B) In vitro–cultured human macrophages, DCs, and T-cell blasts were treated with FITC siLuci alone, transfected with FITC siLuci using Lipofectamine 2000 or transduced with FITC siLuci complexed with RVG-9R or a control RV-MAT-9R peptide, and cells were examined for FITC siLuci uptake by flow cytometry. The experiment was repeated two times with similar results. (C) Cultured macrophages and DCs were transfected/transduced as in B with siRNA targeting cyclophilin B and, after 24 h, tested for cyclophilin B mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. Mean ± SD of triplicates is shown. (D) Splenocytes from humanized mice were examined for FITC siRNA transduction as in A. (E) BLT mice were injected (i.v.) with either control Luci siRNA complexed with RVG-9R or TNF-α siRNA complexed with RVG-9R or a control RV-MAT-9R peptide 18 and 6 h before LPS injection (i.p.). One hour after LPS injection, human TNF-α mRNA levels in PBMCs were tested by qRT-PCR, and serum human TNF-α protein levels were tested by ELISA (Center and Right). Human CD14+ cells in PBMCs of the three groups of mice before the start of the experiment are shown in the left panel. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. *P < 0.05.