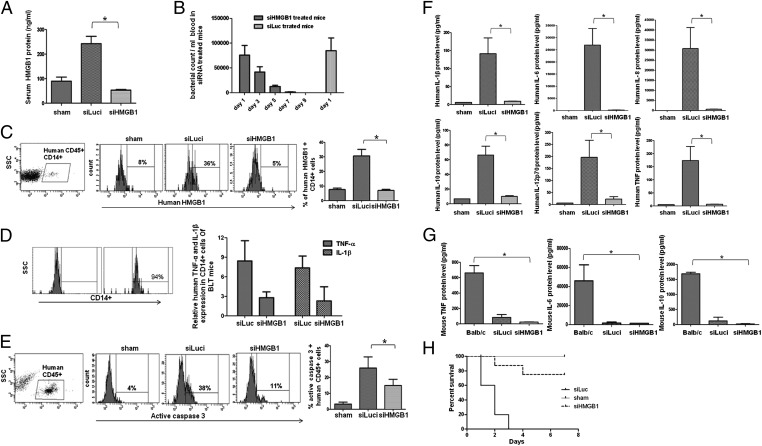
Fig. 3.
Treatment of humanized mice with HMGB1 siRNA/RVG-9R suppresses CLP-induced sepsis. Humanized mice were treated i.v. with either a control Luci siRNA or HMGB1 siRNA complexed with RVG-9R, as detailed in SI Materials and Methods, before and after CLP. Sham indicates sham surgery without CLP or siRNA treatment. (A) Sera obtained 20 h post-CLP were tested for HMGB1 protein levels by ELISA. Mean ± SD from seven mice per group is shown. (B) Bacterial counts in the blood of control and siRNA treated mice at indicated times after CLP are shown. Control mice could not be serially followed because they all died by day 3. (C) Twenty hours post-CLP, splenocytes were tested for HMGB1 expression in human CD45+, CD14+ gated cells by flow cytometry. (Left and Right) Representative flow-cytometric results (Left) and cumulative data from seven mice per group ± SD (Right) are shown. (D) CD14+ cells isolated from control and siRNA-treated mice were tested for TNF-α and IL-1β levels by qRT-PCR (n = 5 per group). (Left) Purity of isolated cells. (E) PBMCs obtained 20 h post-CLP were tested for active caspase-3+ cells within human CD45+ cells by flow cytometry. (Left and Right) Representative flow-cytometric result (Left) and cumulative data from seven mice per group (Right) are shown. (F) Sera obtained 20 h post-CLP were tested for indicated human cytokines by cytometric bead array. Mean ± SD from seven mice per group is shown. (G) Sera obtained 20 h post-CLP were tested for indicated murine cytokines by cytometric bead array. Mean ± SD from seven mice per group is shown. (H) Kaplan–Meier survival curves for mice following CLP is shown (n = 14 per group).