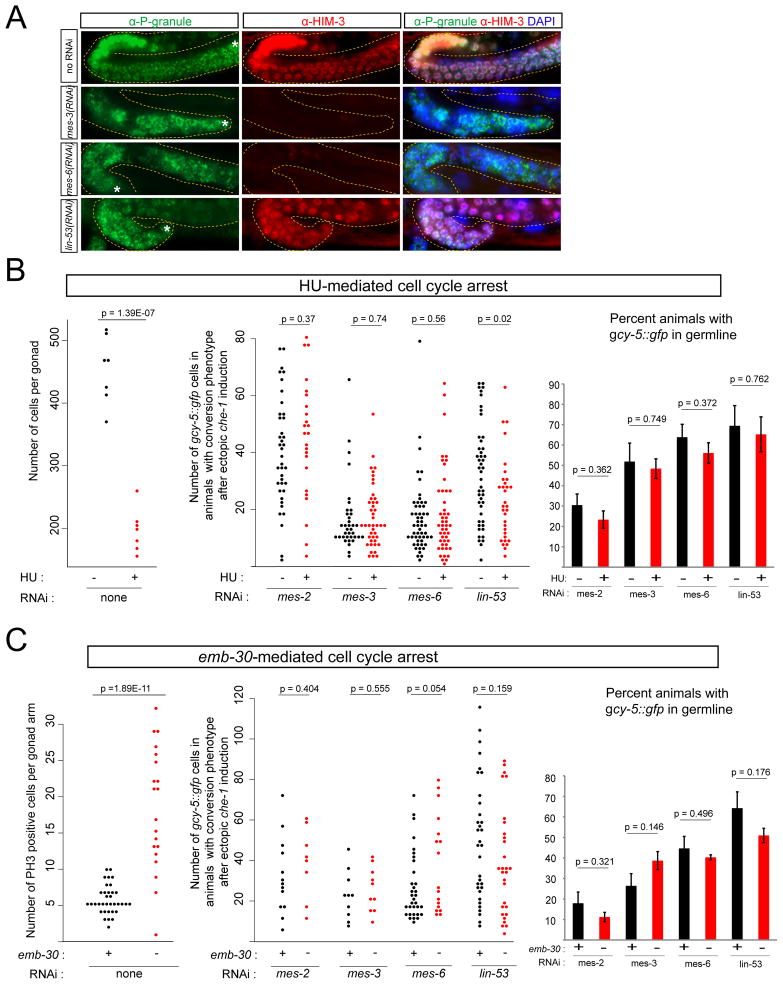
Fig. 3. Mitotic germ cells are converted but mitosis is not required.
(A) RNAi knockdown of MES proteins inhibits entry into meiosis, as assessed by staining with the meiotic marker HIM-3. Knockdown of lin-53 does not completely abolish entry into meiosis. Germ cells were still present in all cases, as assessed by staining with a P-granule specific antibody (OIC1D4). In the case of mes-3(RNAi) and mes-6(RNAi), 80-90% of animals that stained positive for OIC1D4 did not contain HIM-3 positive cells. The remaining 10–20% animals that expressed HIM-3 had healthier-appearing gonads, indicating that RNAi knockdown was inefficient in these worms. Over 90% of lin-53(RNAi) animals that stained positive for OIC1D4, also expressed HIM-3. Asterisks point out the distal most part of the gonad in the image.
(B) Cell cycle arrest by hydroxyurea (HU) treatment. Left panel: reduced number of germ cells in gonads of HU treated animals. Middle panel: expressivity of germline conversion remained unchanged after HU-mediated cell cycle arrest. HU “−” or “+” indicates “no HU treatment” or “5 hours HU treatment” (see Experimental Procedures). Each dot represents an individual animal. The effectiveness of HU treatment was also assessed by the lack of EdU staining (Suppl. Fig. 7). Right panel: The penetrance (i.e. number of animals displaying phenotype) of conversion is also not significantly altered.
(C) Cell cycle arrest by shifting emb-30(tn377ts) mutants to the non-permissive temperature. Left panel: on average, there were about 3 times more germ cells in metaphase after an 8 hour temperature shift. Middle panel: expressivity of germline conversion upon ectopic che-1 induction remained unchanged after emb-30-mediated cell cycle arrest. Each dot represents an individual animal (scored ~24 hours after che-1 induction at the L4 stage). Right panel: The penetrance (i.e. number of animals displaying phenotype) of conversion is also not significantly altered.