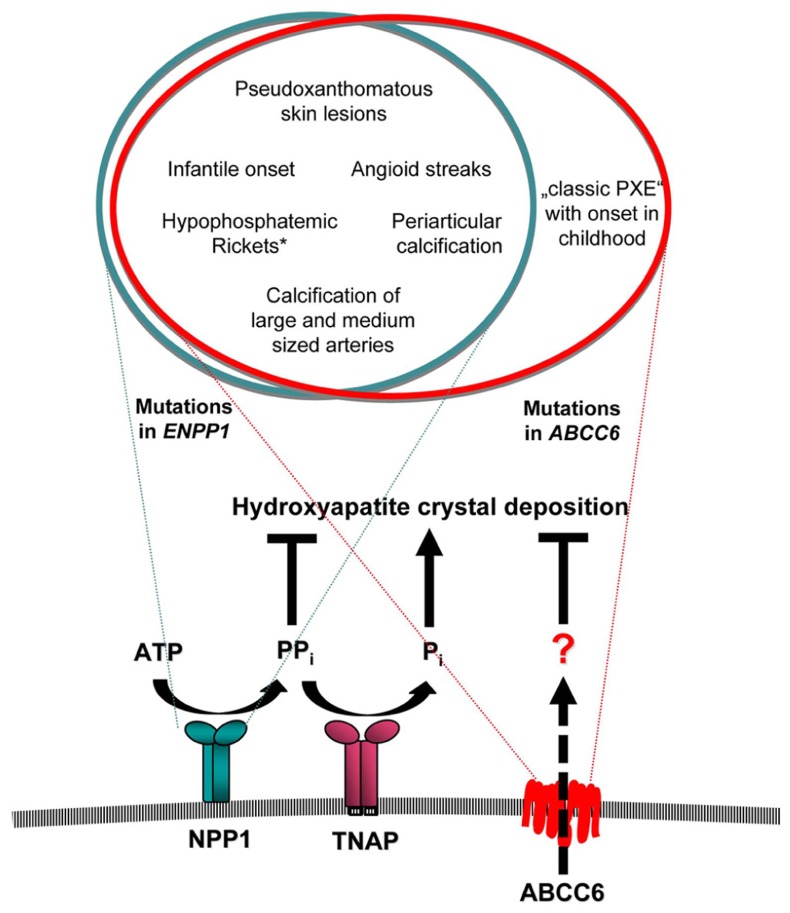
FIGURE 1.
Overlap of clinical manifestations associated with mutations in ENPP1 and ABCC6. NPP1 and ABCC6 serve as a minor component in the function of a network of factors that exert balanced effects to promote and suppress arterial calcification. The transmembrane ectoenzyme NPP1 generates AMP and PPi from ATP. PPi is hydrolyzed by the tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) to generate Pi, which is a component of hydroxyapatite crystal deposition and plays a role in the regulation of osteoblast differentiation. PPi suppresses hydroxyapatite deposition and inhibits ectopic chondrogenesis (and modulates artery calcification by other effects). The role of ABCC6 has to be defined. Mutations of either ABCC6 or ENPP1 can cause the severe phenotype of GACI, which frequently leads to death within the first year of life. While mutations in ENPP1 can also cause typical pseudoxanthomatous skin lesions and angioid streaks of the retina in children with GACI, who survived the critical period of infancy, the later onset of “classic PXE” phenotype without GACI was only observed in patients with mutations in ABCC6. *Hypophosphatemic rickets has been observed frequently in patients with ENPP1 mutations, but was observed only in one proband carrying a mutation in ABCC6 on one allele.