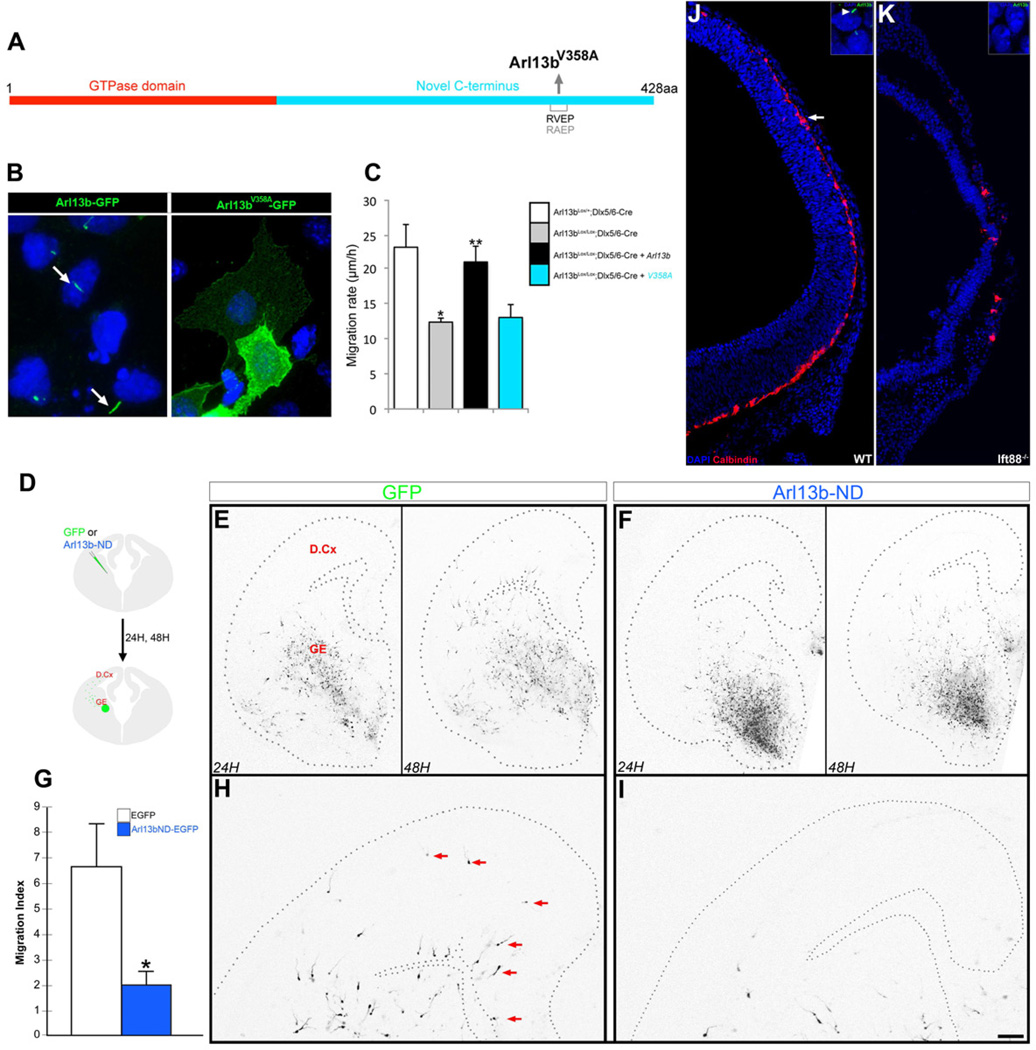
Figure 5. Ciliary function of Arl13b is critical for the regulation of interneuron migration.
(A) Schematic of a non-ciliary form Arl13b (Arl13bV358A). (B) In ciliated IMCD3 cells transfected with control Arl13b-GFP and Arl13bV358A-GFP constructs, Arl13b-GFP localizes to cilia (arrow), but Arl13bV358A-GFP does not. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (C) Expression of wild type Arl13b rescued the migratory defect in Arl13b deficient (Arl13bLox/Lox; Dlx5/6-CIE) interneurons. In contrast, expression of Arl13bV358A did not rescue the defect. Data shown are mean ± SEM (n=42 [Control: Arl13bLox/+; Dlx5/6-CIE], 79 [Arl13b deficient: Arl13bLox/Lox; Dlx5/6-CIE], 104 [Arl13bLox/Lox; Dlx5/6-CIE +Arl13b], 49 [Arl13bLox/Lox; Dlx5/6-CIE+Arl13bV358A]); * indicates significant when compared with controls at p<0.001; ** indicates significant when compared with Arl13b mutant at p<0.001 (Student’s t test). (D-H) Dominant negative N-terminal domain (Arl13b-ND) of Arl13b disrupts selective targeting of Arl13b to primary cilia and inhibits interneuronal migration. (D) Cartoon of experimental protocol. Arl13b-ND/GFP or GFP DNA was focally electroporated into the MGE of E14.5 coronal slices. Images of GFP+ interneuronal migration into dorsal cortex were acquired at 24 and 48 hours. (E-H) Interneurons expressing GFP alone leave the MGE at 24 h (E, left panel) and migrate into the dorsal cortex by 48 h (E, right panel, and higher magnification image of dorsal cortex in H). Interneurons co-expressing Arl13b-ND mostly remain in the GE at 24 h (F, left panel) and show less migration into dorsal cortex at 48 h (F, right panel, and higher magnification image in I). Compared to control (arrows, H), fewer GFP+ interneurons are seen in the dorsal cortex in Arl13b-ND slices (I). (G) Quantification of changes in the extent of interneuronal migration. Migration index indicates the number of cells migrating greater than 350 µm past the GE-dorsal cortex boundary. Data shown are mean ± SEM (n=36 slices/ group); * p<0.05 (Student’s t test). GE, ganglionic eminence; D.Cx, dorsal cortex. (J-K) Disrupted interneuron migration in Ift88−/− brains. (I) Calbindin+ interneurons (red, arrow) migrate from the ganglionic eminence into the dorsal cortex. This migration is severely disrupted in Ift88−/− brain (K). Insets (I, K) show the presence and absence of Arl13b+ cilia in wild type and mutant brains, respectively. Sections were counterstained with DAPI or DRAQ5 (blue). Scale bar= B-C, 34 µm; E-F, 400 µm; H-I, 175 µm; J-K, 180 µm.