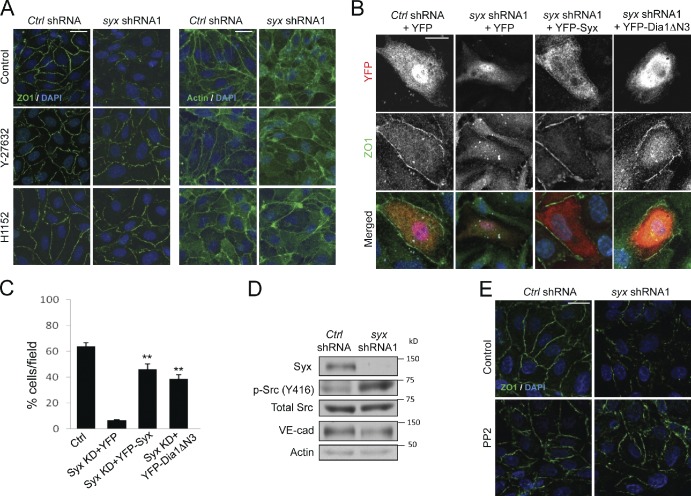
Figure 3.
Dia1 rescues the effects of Syx depletion. (A) Effects of vehicle control, or ROCK inhibition (overnight) with 10 µM Y-27632 or 10 µM H1152 on ZO1 or F-actin (phalloidin) localization in nontarget (control [Ctrl] shRNA) versus Syx-depleted (Syx shRNA1) HUVECs. (B) Effects of transiently expressing YFP alone, YFP-tagged murine Syx (YFP-Syx), or YFP-tagged constitutively active Dia1 (YFP-Dia1ΔN3) on ZO1 pattern in nontarget (control shRNA) versus Syx-depleted (Syx shRNA1) HUVECs. (C) Quantification of the percentage of HUVECs from B that express YFP constructs and are surrounded by a continuous and linear ZO1 staining (means ± SEM; ∼10 cells per field; n = 6; **, P < 0.001). KD, kinase dead. (D) Effect of silencing Syx on Src phosphorylation at Y416 and total VE-cadherin (VE-cad) levels in HUVECs. (E) Effect of vehicle control or Src inhibition (10 min) with 1 µM PP2 on ZO1 localization in nontarget (control shRNA) versus Syx-depleted (Syx shRNA1) HUVECs. Bars: (A and E) 20 µm; (B) 10 µm.