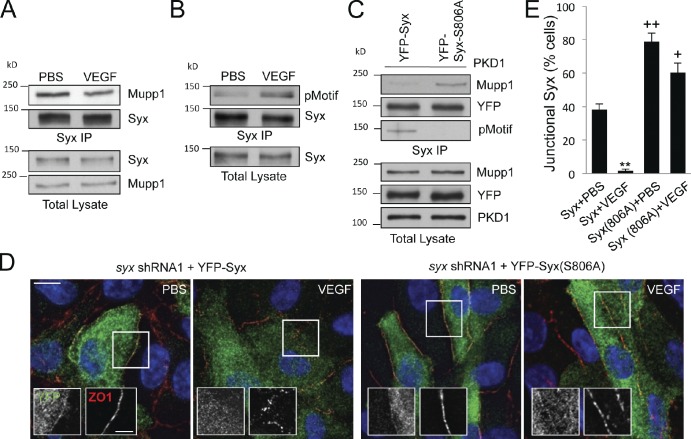
Figure 6.
VEGF and PKD1 regulate Syx binding to Mupp1 and targeting to cell junctions. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous Syx with endogenous Mupp1 in HUVECs treated with either control PBS or VEGF (50 ng/ml for 30 min). (B) Detection of Syx phosphorylation at a classical PKD consensus motif by immunoblotting Syx immunoprecipitates from either PBS- or VEGF-treated cells with the pMotif antibody (pMotif). (C) Effect of the Syx S806A mutation on Mupp1 association. PKD1 was transiently coexpressed together with either YFP-Syx or YFP-Syx-S806A in HeLa cells. Syx was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates using a GFP-specific antibody, and either coprecipitated Mupp1 or PKD-mediated phosphorylation was detected using specific antibodies (Mupp1 and pMotif). (D) Effects of VEGF treatment (50 ng/ml for 30 min) on the localization of ZO1 and ectopically expressed YFP-Syx or YFP-Syx-S806A in HUVECs depleted of endogenous Syx (DAPI; blue). The framed regions of the merged image are also shown as separate YFP and ZO1 images to highlight differences in Syx and ZO1 localization. Bars: (main images) 10 µm; (insets) 5 µm. (E) Quantification of the percentage of HUVECs transfected with YFP-Syx, or YFP-Syx-S806A in fields from D, exhibiting junctional Syx staining (means ± SEM [error bars]; ∼10 cells per field; n = 6; +, P < 0.01; **/++, P < 0.001). IP, immunoprecipitation.