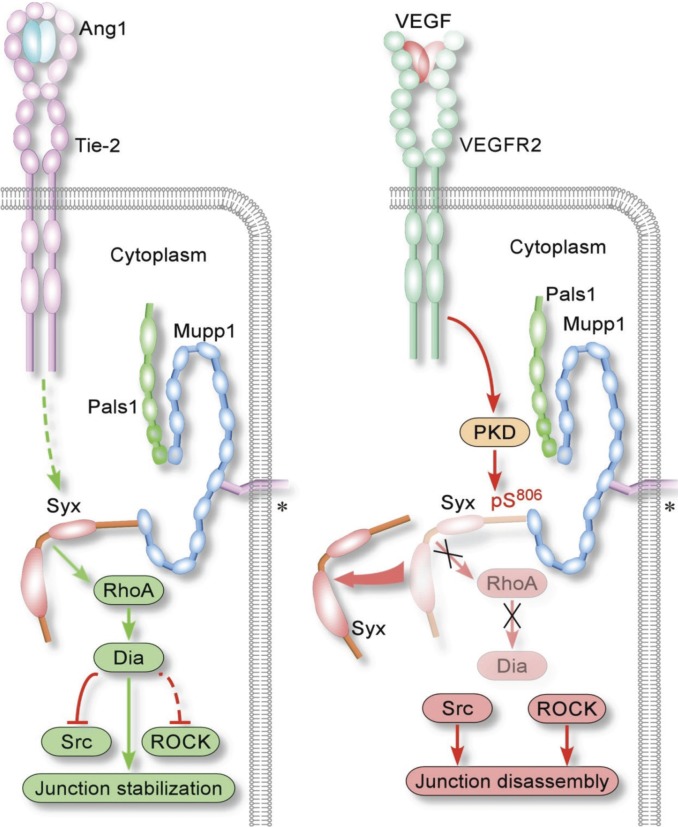
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of Syx action at endothelial junctions. (left) Syx is recruited to endothelial junctions by Mupp1 and forms a complex with multiple members of the CRB polarity complex (the asterisks denote a membrane receptor). This interaction is further promoted by Ang1 and results in the localized activation of RhoA and the selective activation of the Rho effector Dia. Dia induces junction stabilization, at least in part by suppressing the activities of Src and ROCK. (right) In contrast to Ang1, VEGF induces the dissociation of Syx from Mupp1 and its mislocalization away from cell junctions through the PKD-mediated phosphorylation of Syx at Serine 806 (pS806). The loss of junctional Syx/RhoA/Dia signaling results in junction disassembly, through the unopposed activities of Src and ROCK. Junction destabilization increases the permeability of confluent monolayers and induces vascular leakiness.