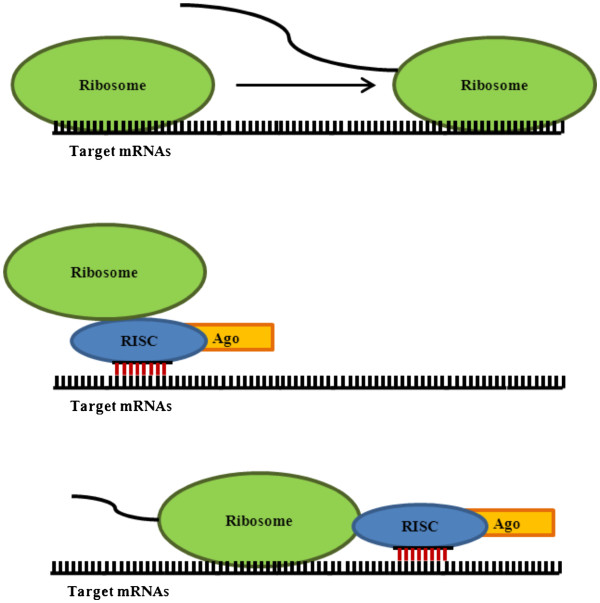
Figure 3.
miRNAs translation repression. Typically, mRNAs is translated into protein by ribosomes (above). However, miRNAs can inhibit this activity through blockade of translation initiation (middle) or post-initiation translation (below). During translation initiation, repression by RISC proteins prevent the association of ribosomes with mRNAs and thereby translation. With post-initiation translation repression, ribosomes associate with the mRNAs but are incapable of completing translation either due to premature disassociation or physical impediment by associated miRNAs. In addition, post-initiation translation repression may occur due to diminished elongation rates as a result of the presence of miRNAs.