Figure 5.
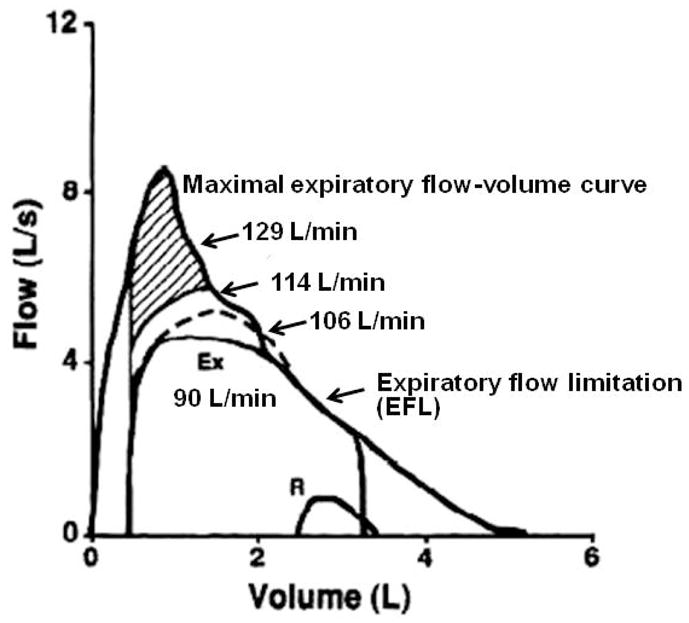
Maximal and tidal expiratory flow-volume curves. Calculated maximal minute ventilation (V̇EL/min) with utilization of greater portions of the maximal expiratory flow curve. If all expiratory reserve was utilized a maximum V̇E of 129 L/min could be obtained. However, except for extreme circumstances or voluntary breathing maneuvers such as the maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV), this is never observed. The curves yielding 114 or 106 L/min are more realistic. Thus, at 90 L/min, ventilatory output is very close to ventilatory capacity. Ex = exercise, R = rest. [Adapted from (11). Copyright © 1993. The American Physiological Society. Used with permission.]
