Figure 4.
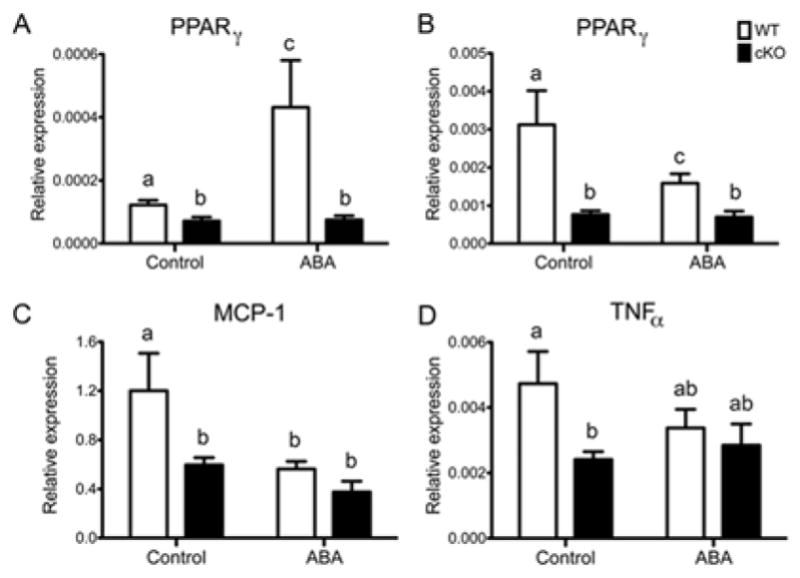
Effect of dietary ABA-supplementation on pulmonary expression of PPAR γ and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) in broncholveolar lavage-derived cells. Cells were collected from the airway of WT or cKO mice 4 days post-infection. Dietary treatment and infection were as described before. ABA treatment increased PPAR γ mRNA expression in healthy non-infected WT mice (A) although following infection WT mice fed the control diet had significantly higher levels of PPAR γ, which correlated with higher mRNA expression of MCP-1 and TNFα, compared to the rest of the groups. Data points with different letters (P<0.05) are significantly different (n=10 mice per treatment and genotype).
