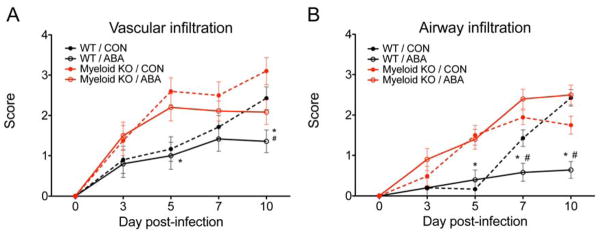
Figure 5.
Effect ABA treatment on vascular infiltration (A) and airway infiltration (B) in the lung following infection with influenza virus. Wild-type (WT) or myeloid-specific PPAR γ null mice (myeloid KO) mice were challenged with 5 x TCID50 of influenza A/Udorn (H3N2) and then treated with either PBS or ABA (100 mg/ABA kg body weight) by oral gavage for 10 days starting on the day of infection. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences between the ABA-treated WT and the myeloid KO mice. Pound signs denote statistically significant differences between the ABA-treated WT and the control WT (n=10 mice per treatment and genotype).