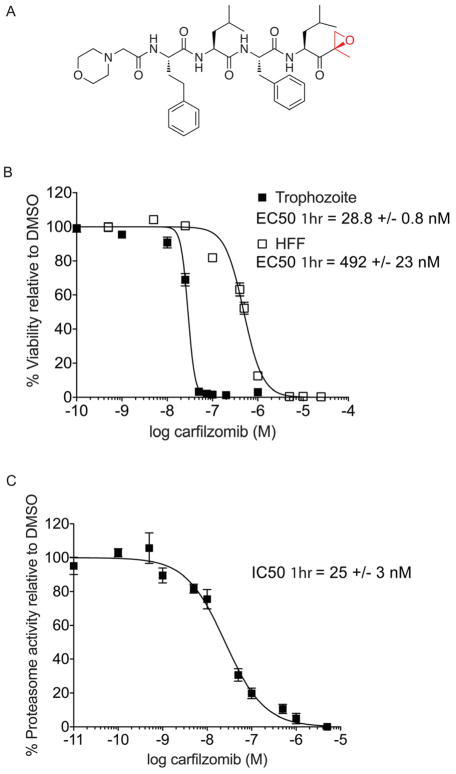
Figure 1.
Anti-parasitic activity and therapeutic window of carfilzomib in vitro. A) Structure of carfilzomib. The epoxyketone reactive functional group is shown in red. B) Dose response of carfilzomib on P. falciparum culture and human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF). Synchronous P. falciparum trophozoites or non-confluent HFF cells were treated for 1 hr followed by washout of the inhibitor and incubation for 60 hr (trophozoite) or 72 hr (HFF). Each concentration was tested at least 3 times; error bars represent standard error of the mean (S.E.M) for each drug concentration from triplicates. EC50 value is shown as mean +/− standard deviation (SD). The dose response curve for 60 hr treatment is shown in Figure S2. C) Proteasome activity in intact trophozoites treated with carfilzomib. Proteasome activity was assessed by monitoring inhibition of the putative β5 subunit (assignment of labeled subunit is shown in Figure S1). Synchronous mid-trophozoite stage parasites were treated with the indicated concentrations of carfilzomib for 1 hr, followed by inhibitor washout and preparation of parasite lysates. Residual proteasome activity of parasite lysate under each drug concentration was determined by labeling with 2 μM MV151. The IC50 curve was obtained from 3 independent experiments; error bars represent S.E.M for each drug concentration from triplicates. A representative probe competition gel is shown in Figure S5. IC50 value is shown as mean +/− standard deviation (SD). (See also Figure S2).