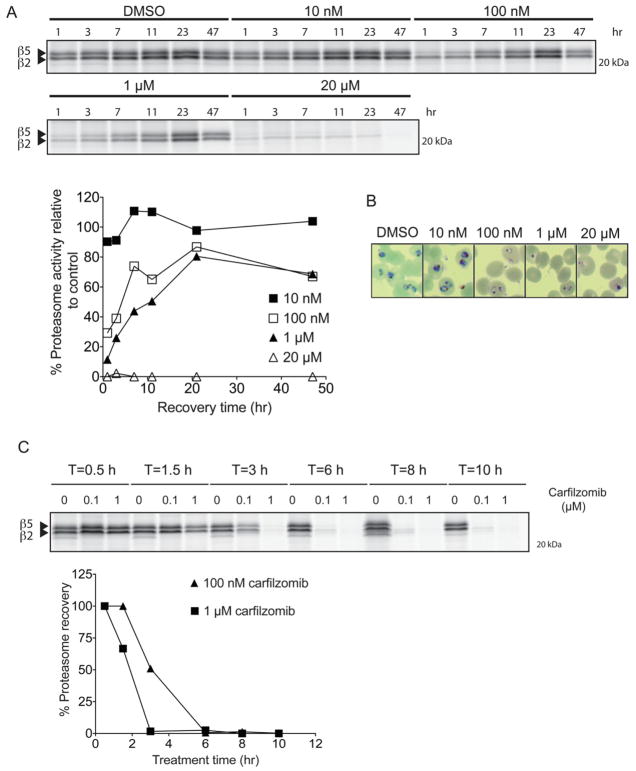
Figure 3.
P. falciparum recovers proteasome activity after a short period of inhibition and prolonged proteasome inhibition prevents recovery. A) Recovery of P. falciparum proteasome activity after 1 hr treatment with carfilzomib. A synchronous culture of trophozoites was treated at the indicated concentrations of carfilzomib for 1 hr followed by extensive washout of the inhibitor. Parasites were kept in fresh media for a further 47 h, and proteasome activity in lysates obtained at different time points was determined by labeling with MV151 (see Figure S1). To adjust for variation of proteasome content due to parasite growth, proteasome activity was normalized to DMSO treated parasites obtained at each respective time point. Proteasome activity at each time point was assessed by intensity of probe labeling. Quantification of the putative β5 subunit labeling is shown in the graph below the gel image. B) Giemsa-stained thin blood smears of P. falciparum culture treated with carfilzomib for 1 hr followed by 47 hr washout. C) Synchronous trophozoites were treated with 100 nM or 1 μM carfilzomib for the indicated times followed by inhibitor wash out. Parasites were placed in fresh media, and proteasome activities of all samples were determined by MV151 labeling at 10 hr after inhibitor washout. Quantification of the putative β5 subunit labeling is shown in the graph below the gel image. (See also Figure S1)