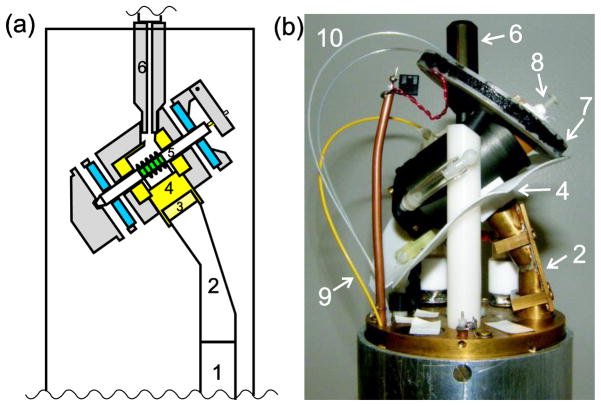
Figure 1.
He-cooled DNP MAS probe: (a) Cross-section view of probe head. The sample is shown in green, the bearings in blue, Teflon parts in yellow, and other plastic parts in grey. (b) Photograph of the probe head. Microwaves enter the bottom of the probe by reflection from a mirror on the optical table [30] into a corrugated waveguide (1), which leads to a miter bend (2) to direct the microwaves towards the MAS assembly. To reach the sample, the microwaves pass through a Teflon lens (3), a Teflon coil holder (4), the RF coil, and the zirconia rotor (5). Cold helium from a vacuum-insulated stainless steel transfer line enters the MAS assembly through a Torlon tip (6). Also visible are the shim coil (7), hinged pointer for stabilizing spinning (8), fiber optic temperature sensor (9), and optical fibers for detection of MAS rate (10).