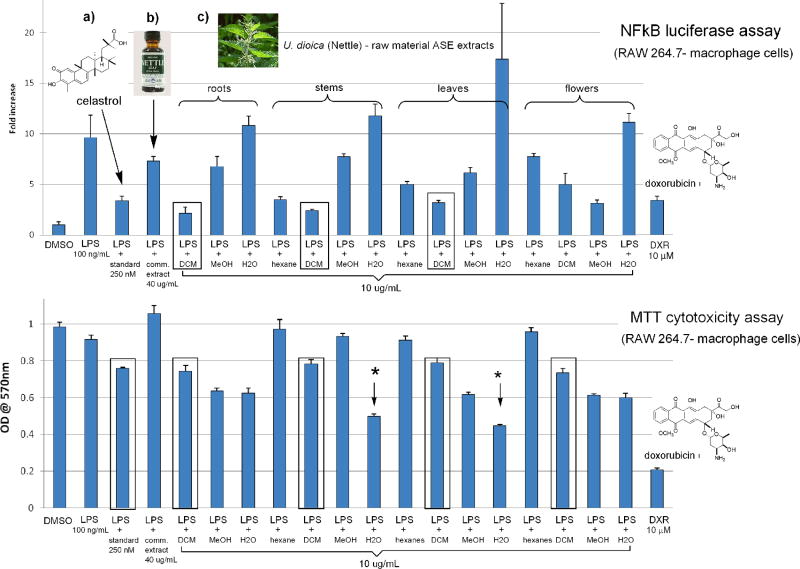
Figure 2.
Comparative bioassay data of: (a) standard NF-κB inhibitor (celastrol, 1); (b) a commercial ethanol leaf extract of U. dioica (stinging nettle) and (c) ASE extracts of U. dioica evaluated in the NF-κB luciferase and MTT cytotoxicity assays. The upper row depicts anti-inflammatory activity measured by the NF-κB assay. Samples with more potent anti-inflammatory activity are indicated by shorter graph bars. The bottom row gives the results of the MTT cytotoxicity assay. In this representation, shorter bars indicate greater cytotoxicity.