Figure 1. Iodide decreases Na+/I− symporter (NIS)-mediated I− uptake.
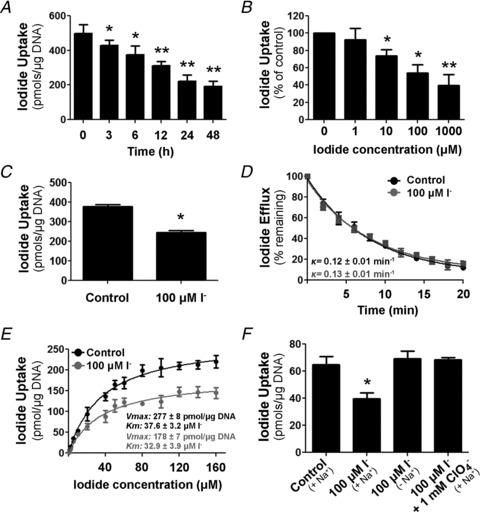
A, steady-state I− uptake in IEC-6 cells incubated with 100 μm I− for 3–48 h. Uptake was expressed as picomoles of I− per microgram of DNA. Each value represents the mean ± SD of five independent experiments done in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005 vs. control (time 0 h; ANOVA and Newman–Keuls test). B, steady-state I− uptake in IEC-6 cells treated with 1–1000 μm I− for 24 h. The results are expressed as a percentage of non-I−-treated uptake levels for each I− concentration. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments done in triplicate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control (time 0 h; ANOVA and Newman–Keuls test). C, steady-state I− uptake levels in IEC-18 cells incubated with 100 μm I− for 24 h. Each value represents the mean ± SD of two independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P < 0.005 vs. control (ANOVA and Newman–Keuls test). D, I− efflux in IEC-6 cells treated with 100 μm I− for 24 h. Results are plotted as a percentage of the remaining intracellular I−. Decay constants (k) for control and I−-treated cells are indicated. E, initial rates (2 min time points) of I− uptake at different I− concentrations (ranging from 0 to 160 μm) in the presence of a constant Na+ concentration (140 mm). Data were analysed using the following equation: v= (Vmax*[I−])/(Km+[I−]) and fitted by non-linear least squares using Gnuplot software. Kinetic parameters were determined in triplicate and expressed as means ± SD. *P < 0.05 vs. control Vmax (Student's unpaired t test). F, IEC-6 cells were incubated in buffered Hanks’ balanced salt solution containing 100 μm I− in the presence or absence of 1 mm ClO4− for 6 h, where osmolarity was maintained by either Na+ or choline+. After treatment, cells were extensively washed to remove remaining free I−, and steady-state I− transport was assessed. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments done in triplicate. *P < 0.01 vs. 100 μm I− (140 mm choline+; ANOVA and Newman–Keuls test).
