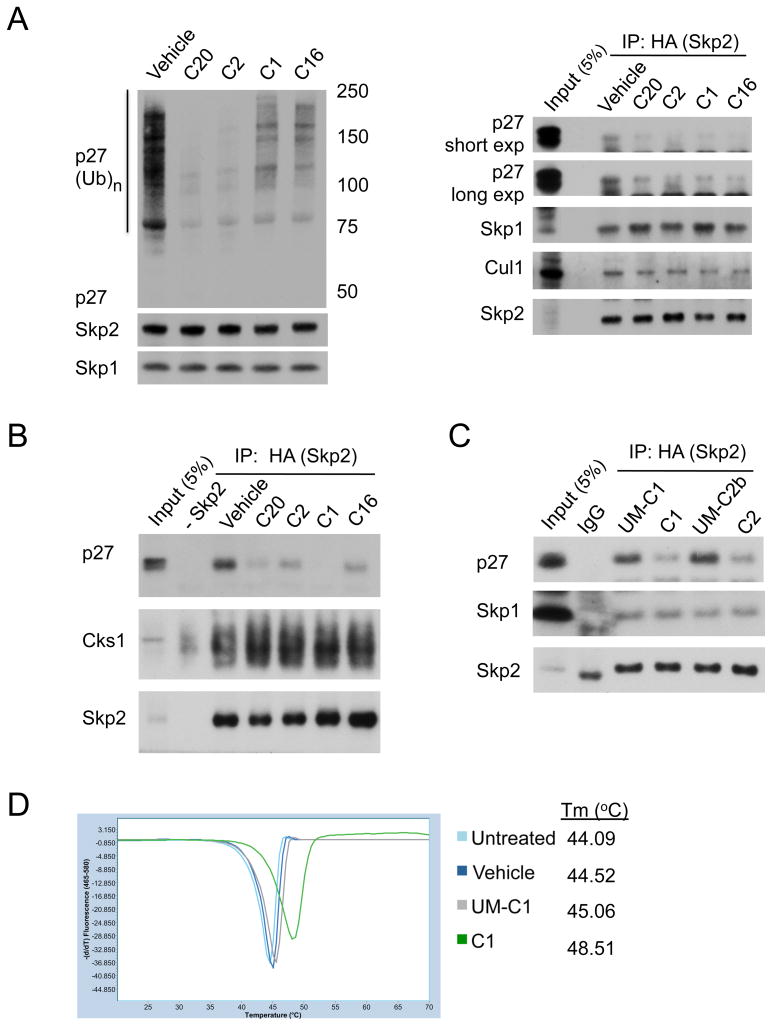
Figure 3. Binding of inhibitors disrupts the Skp2-p27 interaction.
(A) Reduced ubiquitylation correlates with reduced interaction. (Left) Immunoblotting for p27, Skp2, and Skp1 from ubiquitylation assays treated with Vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or 10 μM inhibitor (C20, C2, C1, or C16). (Right) Immunoblotting for p27, Skp1, Cul1, and HA-Skp2 in HA immunoprecipitates from ubiquitylation reactions.
(B) Inhibitors reduce p27 binding to Skp2. HA-Skp2 and Cks1 were pretreated with Vehicle (0.1%DMSO) or 10 μM inhibitor (C20, C2, C1, or C16) before added to p27-pT187. HA-immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for p27, Cks1, and Skp2.
(C) Loss of chemically active groups restores p27 binding. HA-Skp2/Cks1 was pretreated with 10 μM inhibitor (C1 or C2) or corresponding unmatched compound (UM-C1 or UM-C2b, see Figure S3A) before p27-pT187 addition. HA-immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for p27, Skp1, and Skp2.
(D) Loss of active groups removes compound binding. Melting temperature (Tm) of recombinant His-6Skp1-Skp2-Cks1 (1.5 μM) preincubated with C1 (75 μM), UM-C1 (75 μM), or Vehicle (0.5% DMSO) determined from melting peaks using differential scanning fluorimetry.
See also Figure S3.