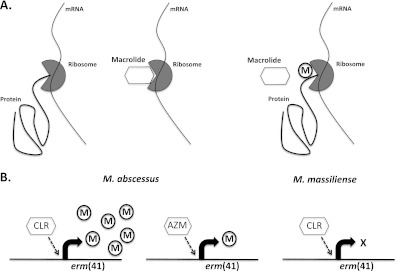
Figure 1.
Mechanism of macrolide action and inducible macrolide resistance. (A) Macrolide antibiotics bind to the 23S ribosomal RNA, preventing bacterial protein synthesis. Expression of erm (erythromycin resistance methylase) proteins in response to macrolides leads to modification of their ribosomal binding site and induction of macrolide resistance. (B) Induction of erm(41) and subsequent macrolide resistance is greater after exposure to clarithromycin (CLR) than to azithromycin (AZM) in Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies. However, neither macrolide can induce resistance in M. massiliense, because it carries a defective erm(41) gene.