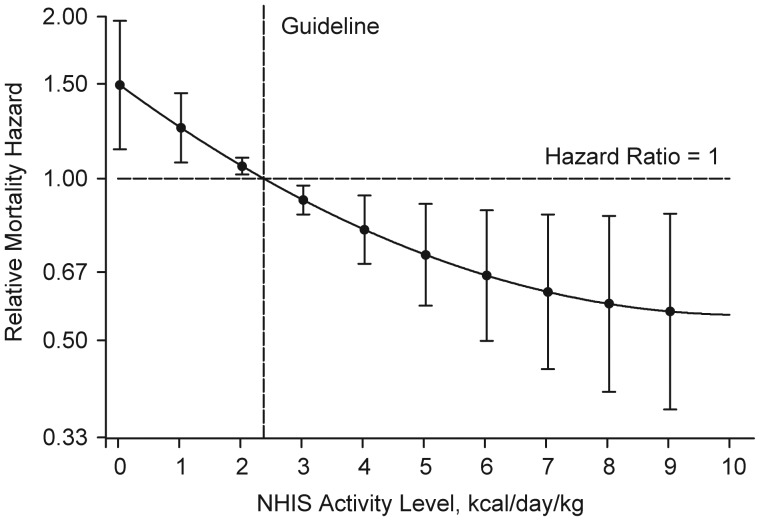
Figure 1.
Relation between National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) physical activity level at baseline and 10-year all-cause mortality rate adjusted for age, race, and educational level among women in the Women's Health and Aging Study II (1994–2009) who reported any activity at baseline (n = 401). Shown are relative hazard estimates for mortality linked to specific activity levels compared with the hazard linked to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/American College of Sports Medicine recommended 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week (equivalent to approximately 1,000 kcal/week for an individual weighing 60 kg or 2.38 kcal/day/kg, as denoted by the vertical dashed line). The curve represents the age-, race-, and educational level-adjusted relative mortality hazards across activity levels, and the bars indicate their 95% confidence intervals. The y-axis was transformed so that, for example, the graphic display of an increase in risk of the magnitude of 2 (hazard ratio = 2) would be equivalent to that of a decrease in risk of the same magnitude (hazard ratio = 0.5) in terms of scale size.