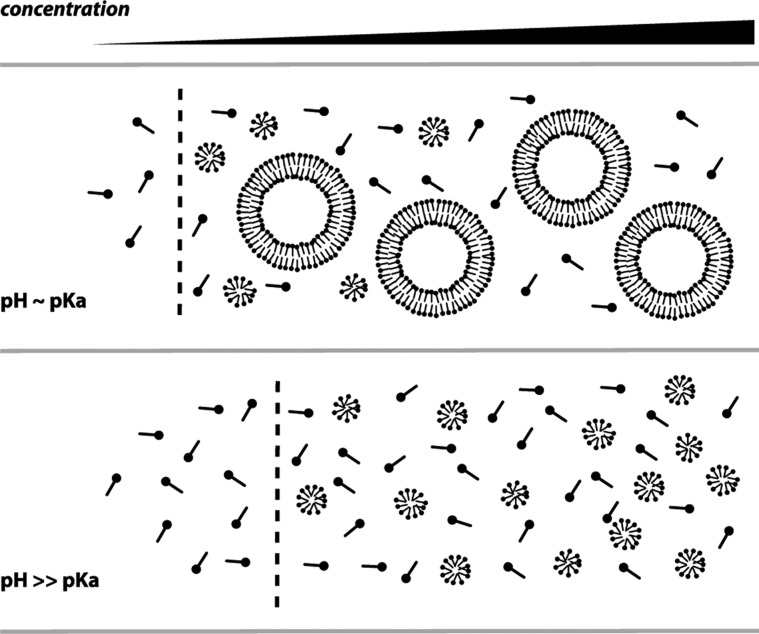
Figure 9.
Model for fatty acid phase behavior. Solutions feature a pseudophase separation from monomers to aggregates, characterized by a cac (dashed line) that is dependent on pH. In addition, vesicle solutions feature a concentration-dependent vesicle–micelle equilibrium, with higher concentrations favoring the larger vesicle aggregates. In contrast, alkaline solutions exhibit a single sharp pseudophase transition at the cmc. Both pH and concentration-driven phase transitions can drive fatty acid vesicle growth.