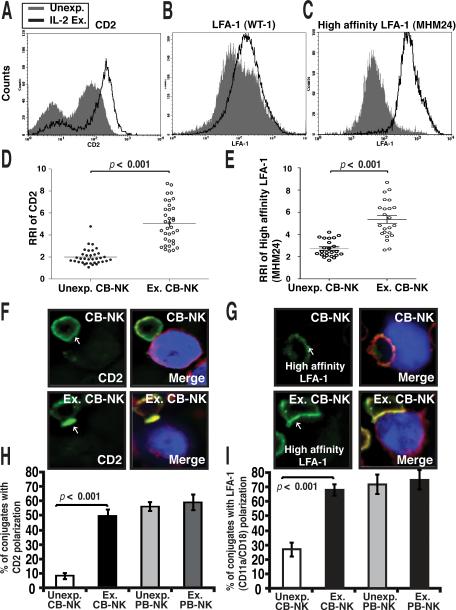
FIGURE 4.
Enhanced recruitment of CD2 and LFA-1 to CB-NK cell immune synapses following ex vivo IL-2 expansion. A, Representative flow cytometric analysis (one of six) of CD2 (A), LFA-1 (WT-1 mAb) (B), and high-affinity LFA-1 (MHM24 mAb) (C) expression on unexpanded (Unexp., gray-shaded histogram) compared with IL-2-expanded (Ex., black line) CB-NK cells. D and E show quantitative image analysis (relative recruitment index, RRI) of CD2 (D) and high-affinity LFA-1 (MHM24 mAb) (E) at the NK cell immunological synapse for unexpanded compared with expanded CBNK cells. Each dot represents a CB-NK cell synapse (50 conjugates analyzed per experiment). The black bar shows the mean value SEM F and G, Confocal images of CB-NK and expanded CB-NK conjugates with AML blasts (blue) stained with CD2 antibody conjugated with Alexa-488 dye (green) or the high-affinity LFA-1 antibody (MHM24) conjugated with Alexa-488 dye (green) and F-actin (red). Arrows indicate protein localization at the NK cell-AML blast synapse site. Co-localization of proteins in the merged images is shown in yellow. Original magnification 40×. H and I, Unexp. and Ex. CB-NK and PB-NK conjugates with AML blasts were scored for polarization of CD2 (H) or LFA-1 (I). Values are the means ± SEM from six independent experiments, with at least 50 random conjugates analyzed per experiment.