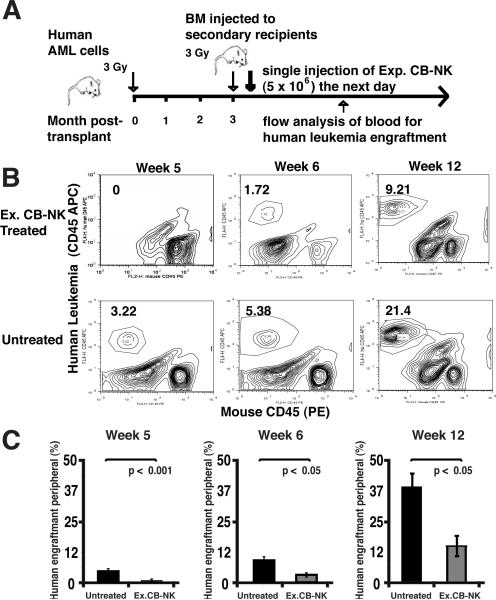
FIGURE 7.
IL-2-expanded CB-NK cells exhibit potent in vivo anti-leukemic effector function by inhibition of primary human AML cells engraftment in NOD-SCID-IL2Rγnull mice. A, Schematic summary of in vivo functional studies using expanded CB-NK cells with a NOD-SCID-IL2Rγnull model. BM, bone marrow. B, Representative flow cytometric analysis showing the percentage of CD45+ human leukemia cells detected in the peripheral blood of a control (saline treated) mouse versus a mouse treated with expanded (Ex.) CB-NK cells. Data are shown from weeks 5, 6, and 12 after CB-NK cell administration. C, The cumulative flow cytometric analysis of treated mice at weeks 5, 6, and 12 after infusion of IL-2 Ex. CB-NK cells compared with the control (saline treated) group is shown. Bars represent the percentage of human leukemia in the peripheral blood obtained from the control group (black bars) versus the Ex. CB-NK treated group (gray bars). Values are means ± SEM for 6 mice. Data show one of two independent studies using human AML primary cells.