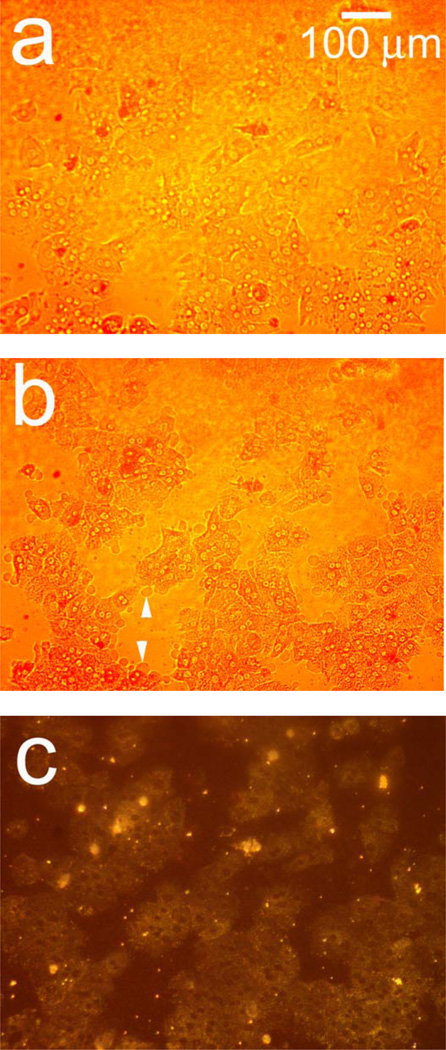
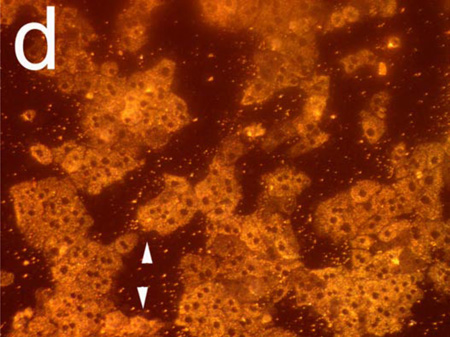
Figure 2.
Observation of morphology changes in a monolayer of primary rat hepatocytes resident on a polystyrene-filled porous Si photonic crystal using optical microscopy. Cells are monitored before and after exposure to a toxic dose of aqueous cadmium chloride (Cd2+). Hepatocytes (a) before and (b) after exposure to 200 µM aqueous Cd2+, obtained with the illumination source and observation axis coincident with the surface normal to the chip, as illustrated in Figure 1a. The same set of hepatocytes (c) before and (d) 85 min. after exposure to 200 µM aqueous Cd2+, but obtained in the scattering configuration indicated in Figures 1c and 1d, in which light is incident from an off-normal white light source. The arrows in (b) indicate blebbing, a common feature found for unhealthy mammalian cells. Blebbing does not appear to contribute to the scattering signal, as is evident by the fact that the feature cannot be distinguished in the scattering configuration (d).