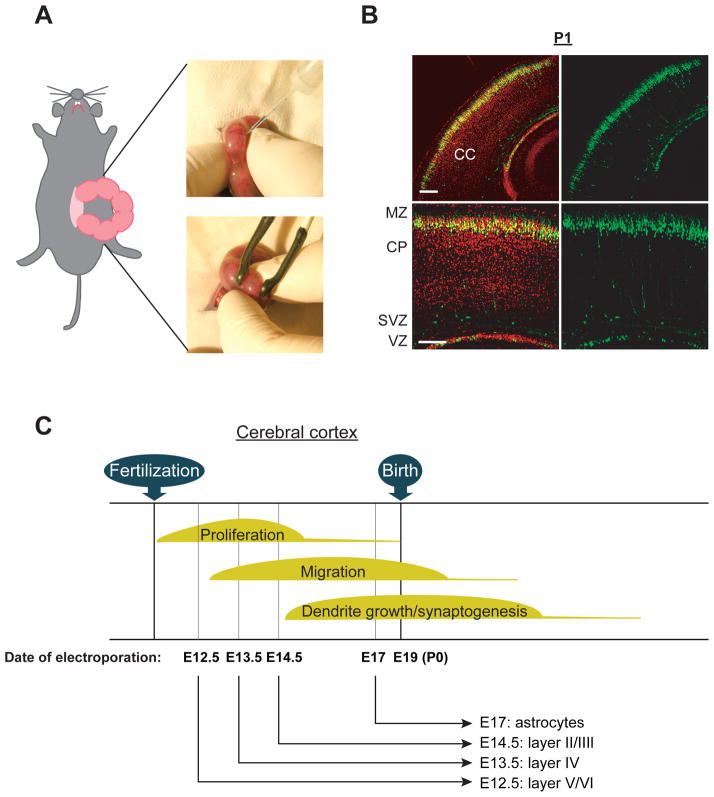
Figure 2. Genetic manipulation via in utero electroporation in selective cell population in the cerebral cortex.
(A) Images displaying injection of DNA solution into lateral ventricle followed by gene delivery into the ventricular zone (VZ) via electroporation by holding the embryos with forceps-type electrodes.
(B) Representative images of GFP-positive cells distributed at the cortical plate (CP) in the cerebral cortex at postnatal day 1 (P1); GFP expression constructs were introduced at embryonic day 15 (E15). CC, cerebral cortex; MZ, marginal zone; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Red, Nucleus. Scale bars, 100 μm. Adapted from the Kamiya (Kamiya 2009).
(C) Schematic representation of the genetic manipulation in the selective cell population in the cerebral cortex. Electroporation directed into progenitor cells in the neocortical ventricular zone at E12.5, E13.5, E14.5, and E17 allows for the modulation of gene expression in a lineage of pyramidal neurons in the layer V/VI, layer IV, layer II/III, as well as astrocytes, respectively.