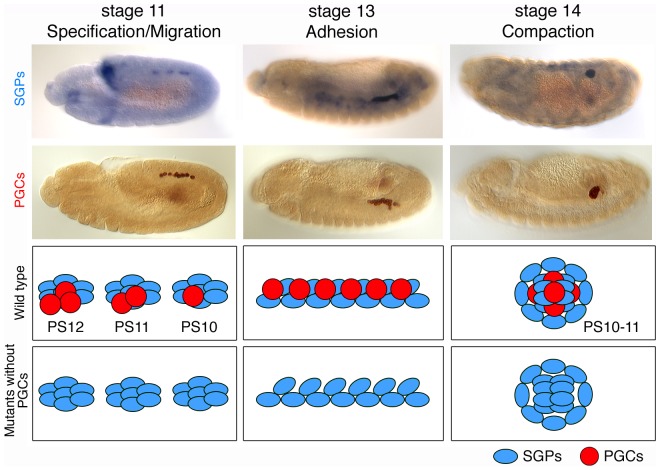
Figure 1. Schematic drawing of gonad formation in wild type and mutants without PGCs.
(Top and middle panels) Gonad coalescence in wild type. SGPs (blue) are specified as three clusters in parasegments (PSs) 10–12. At stages 11–12, PGCs (red) migrate to associate with somatic gonads. At stage 13, SGPs and PGCs align in the future gonad region. At stage 14, SGPs and PGCs undergo compaction to form the embryonic gonad. (Bottom panels) Normal gonad coalescence in mutants without PGCs. In the absence of PGCs, SGPs are specified normally and are able to complete gonad coalescence.