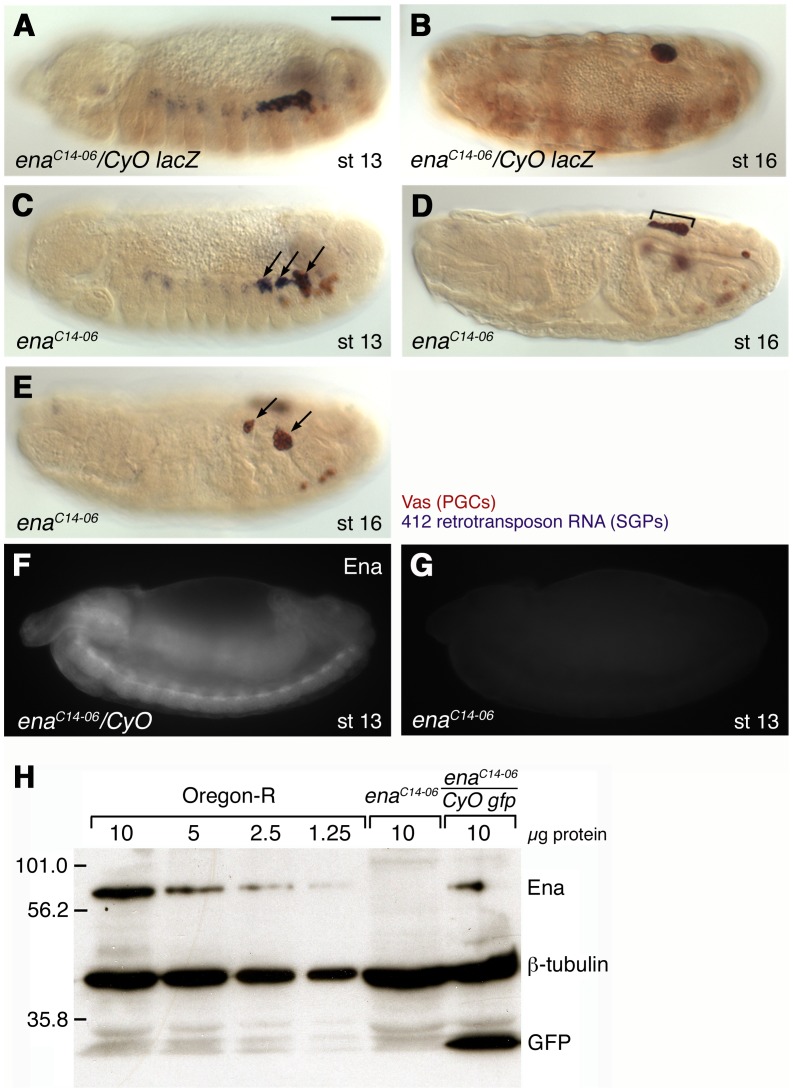
Figure 2. The enaC14-06 allele affects gonad coalescence.
(A–E) SGPs were detected by in situ hybridization with a 412 retrotransposon RNA probe (blue). PGCs were labeled with anti-Vasa (Vas) antibody (brown). The brown signal in a segmental pattern is β-galastosidase from the balancer chromosome. In wild type, individual SGP clusters align with PGCs at stage 13 (A) and undergo coalescence to form tightly associated embryonic gonads at stage 14 to 16 (B). In enaC14-06 mutants, individual SGP clusters fail or delay to adhere at stage 13, remaining instead in three clusters (arrows in C). Subsequently, mutant gonads fail to complete coalescence resulting in elongated (bracket in D) or split gonads (arrows in E). (F–H) Ena protein detected with anti-Ena antibody. Ena protein is expressed ubiquitously in the wild type (F). Ena protein was not detected in enaC14-06 mutants either by tissue-immuno fluorescence (G) or Western blotting (H). Scale bar in (A) represents 50 µm.