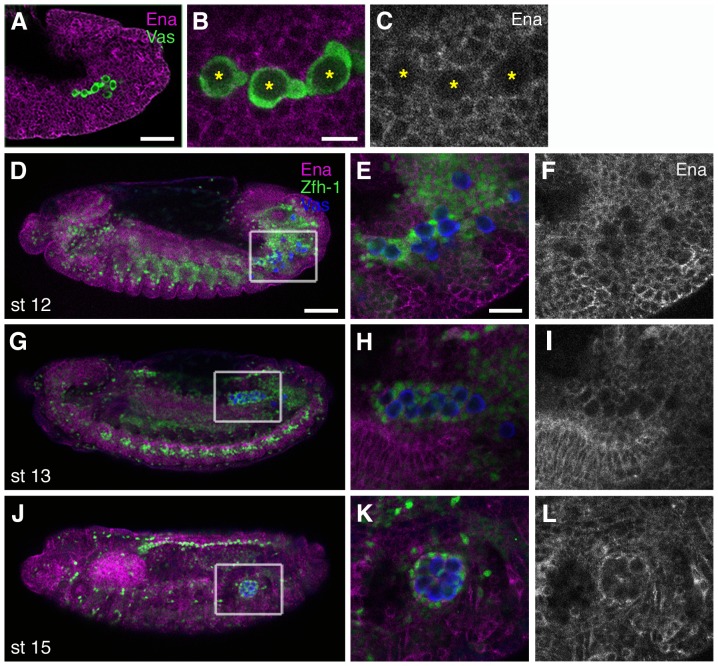
Figure 3. Ena is expressed in the SGPs during gonad coalescence.
(A–C) Stage-12 embryo stained with the anti-Ena antibody (magenta in A–B, white in C) and anti-Vas antibody to detect PGCs (green). The posterior half of the embryo is shown in (A), migrating PGCs are magnified in (B, C) (asterisks). Ena protein is found at the cell membranes (A) but not in migrating PGCs (B, C). (D–L) Ena expression during gonad coalescence. Wild-type embryos were stained with anti-Ena (magenta), anti-Zfh-1 antibodies, which mark the nuclei of the fat body and SGPs (green), and anti-Vas (PGCs in blue). Ena levels in the SGPs were indistinguishable from those in the surrounding tissues (D, high magnification in E, F). Ena expression in the SGPs was more pronounced in the mature gonad (G, J, high magnification in H–I and K–L). The scale bars in (A and D), (B), and (E) represent 50 µm, 10 µm, and 20 µm, respectively.