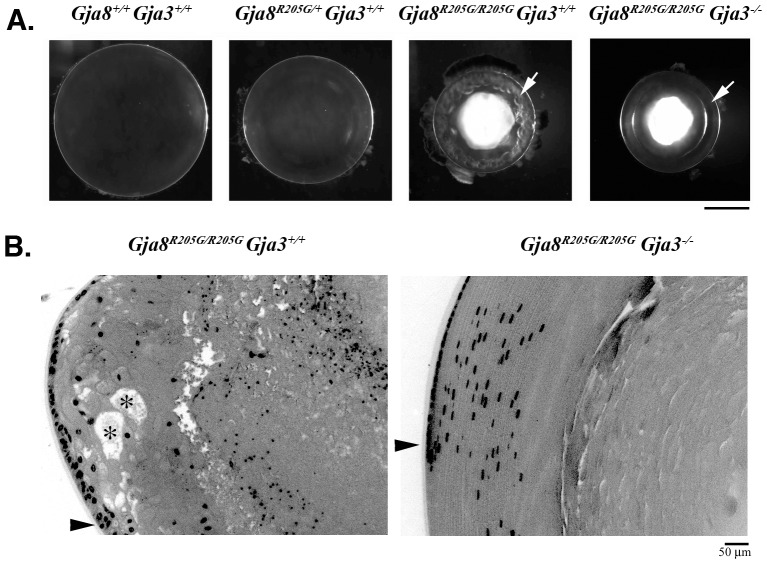
Figure 2. Endogenous Cx46 influences cataract formation caused by the Gja8R205G mutation.
(A) Lens photos of wild-type (Gja8+/+ Gja3+/+), Gja8R205G heterozygous (Gja8R205G/+Gja3+/+), Gja8R205G homozygous (Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3+/+), and Gja8R205G Gja3 double mutant (Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3−/−) mice at the age of 3 weeks. These mutant lines were bred into the C57BL/6J strain background. While the Gja8R205G homozygous (Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3+/+) lens revealed vacuole-like defects in the lens periphery (indicated by a white arrow), the Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3−/− double mutant lens showed a clear lens periphery (indicated by a white arrow). Scale bar, 1 mm. (B) Histological sections of Gja8R205G homozygous mutant (Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3+/+) and Gja8R205G Gja3 double mutant (Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3−/−) lenses from 3-week-old littermates. The Gja8R205G/R205G Gja3+/+ lens section showed disorganized peripheral fibers with vacuoles or enlarged extracellular spaces (labeled with asterisk) near the lens bow region (indicated by an arrowhead), while the double mutant lens section shows organized and elongated periphery fiber cells at the bow region (indicated by an arrowhead). Scale bar, 50 µm.