Figure 3. Dcp2 mutant flies fail to develop cNILH.
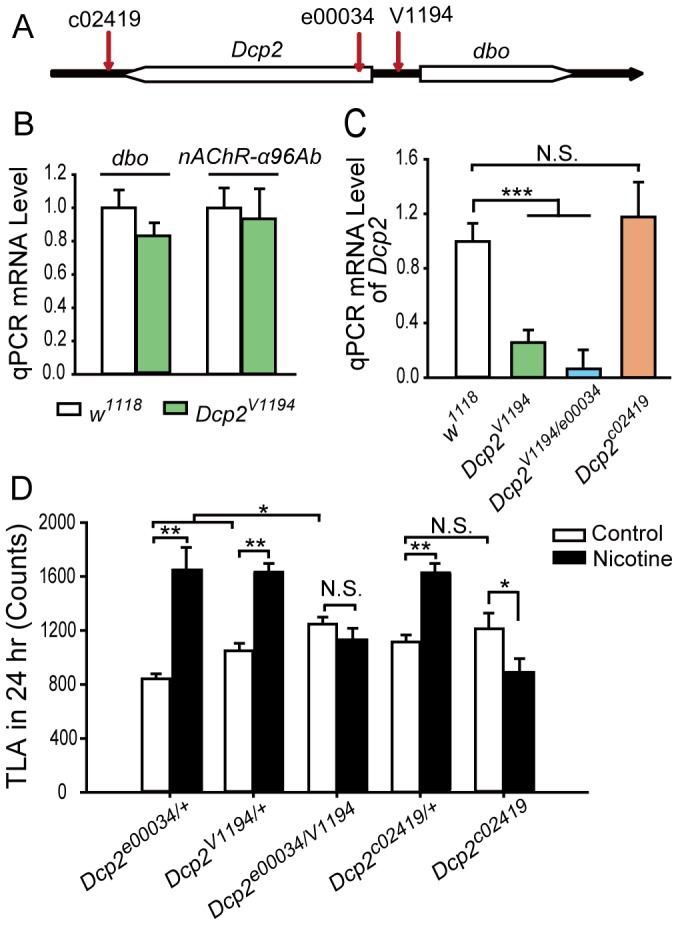
A. Diagram of the Dcp2 genomic region with gene direction. The red vertical arrows indicate the P-element insertion sites of the Dcp2V1194, Dcp2c02419, and Dcp2e00034 mutant alleles. B–C. Total RNA extracted from fly bodies was analyzed for dbo, nAChR-α96Ab and Dcp2 mRNA levels by relative qPCR. The mRNA levels of the tested genes were normalized to rp49 mRNA. (B) The mRNA levels of dbo and nAChR-α96Ab were not altered in the Dcp2V1194 flies compared to the w1118 flies (three independent experiments, N.S., P>0.05, t-test). (C) Dcp2 mRNA levels were reduced in both Dcp2V1194 and Dcp2V1194/e00034 flies (***P<0.001) but not in Dcp2c02419 flies (N.S., P>0.05), compared to w1118 flies. Three independent experiments were performed, one-way ANOVA. D. The locomotor activity of flies treated with nicotine-containing or control food for 4 days was recorded on the 4th day. Total locomotor activity (TLA) data shows cNILH in heterozygous mutant Dcp2V1194/+, Dcp2c02419/+, and Dcp2e00034/+ flies (**P<0.01), but not in trans-heterozygous mutant Dcp2V1194/e00034 and homozygous mutant Dcp2c02419 flies (N.S., P>0.05) (Mann-Whitney U test). Dcp2c02419 flies showed significantly decreased TLA (*P<0.05). Basal TLA of Dcp2V1194/e00034 flies was significantly higher than that of Dcp2V1194/+ or Dcp2e00034/+ flies (*P<0.05), but comparable in Dcp2c02419 and Dcp2c02419/+ flies (N.S., P>0.05) (One-way ANOVA). n = 28–32. N.S. indicates no significant difference. Bars and error bars represent the mean ± SEM.
