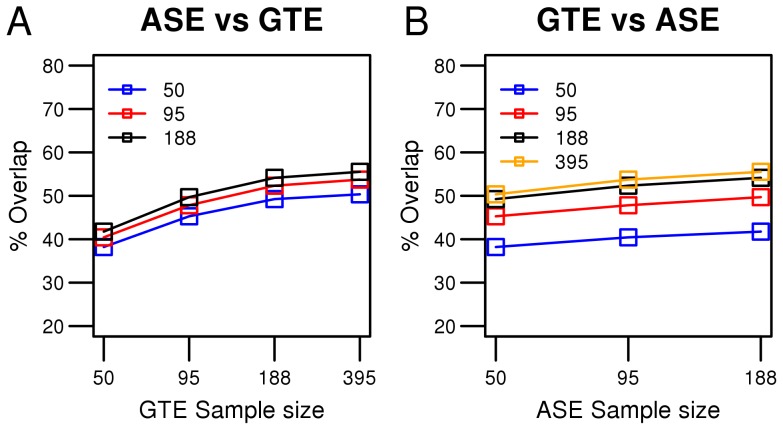
Figure 1. Overlap of significantly associated rSNPs identified by ASE and GTE.
The percentage of overlapping rSNPs detected by allele-specific expression (ASE) and genotype expression (GTE) analysis is plotted for varying numbers of samples. The top 9536 SNPs from the GTE analysis are compared with the top 38203 SNPs from the ASE analysis, which corresponds to a Bonferroni threshold of p = 0.05 for a GTE sample size of 395 and an ASE sample size of 188. The p-value cut-offs were adapted so that the same SNP top-list sizes were obtained at all sample sizes for both GTE (p-value of 1.17E-7, 1.06E-4, 1.93E-3, 6.12E-3 for n = 395, n = 188, n = 95, and n = 50 respectively) and ASE (p-value of 8.06E-8, 9.35E-5, 4.90E-3 for n = 188, n = 95, and n = 50 respectively). The vertical axes show the percentage of SNPs in the top-lists detected by both GTE and ASE analysis and the horizontal axes show the number of samples analyzed using GTE and ASE, respectively. The percentage overlap is calculated by dividing the number of overlaps with the number of top SNPs in the GTE analysis. In (A), each line shows the effect on the number of overlapping SNPs detected by ASE analysis of a specific sample size when the sample size in GTE analysis was increased. In (B), each line shows the effect on the number of overlapping rSNPs detected by GTE analysis of a specific sample size when the samples size in ASE analysis is increased.