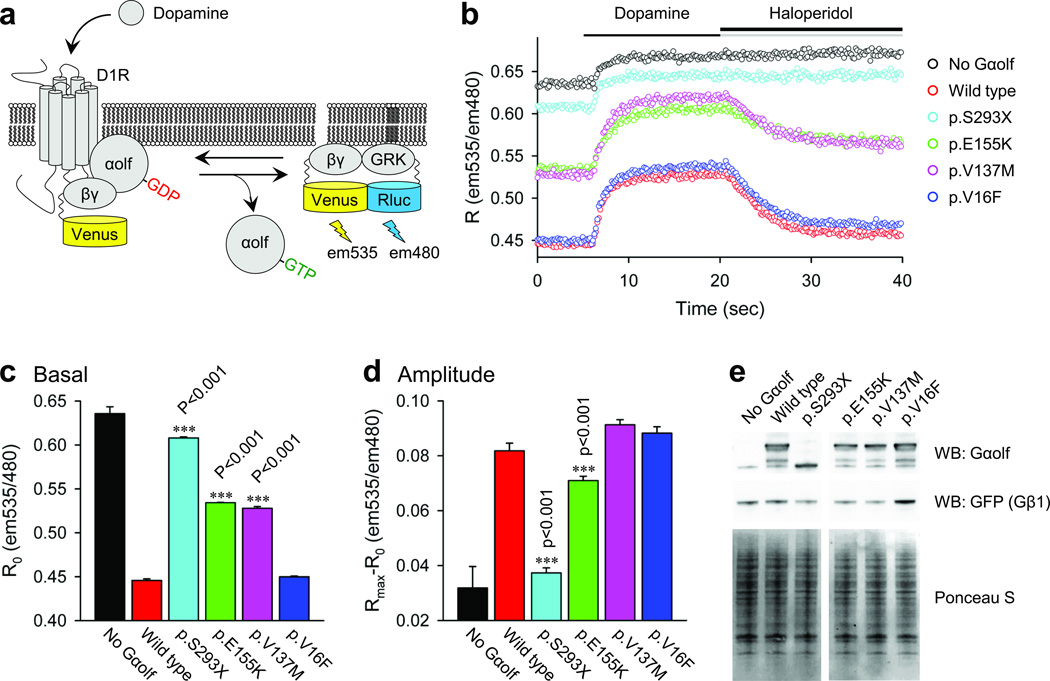
Figure 2.
Effect of mutations on Gαolf coupling to D1R. a. Schematics of the assay design. Stimulation of the D1R by dopamine results in the dissociation of Gαolf from the heterotrimer. Released Gβγ subunits tagged with Venus become available for the interaction with Rluc8-tagged GRK reporter producing the BRET signal which is determined by the change in the emission ratio at wavelengths 535nm and 480nm. b. Time course of the BRET signal change upon stimulation of cells with dopamine and subsequent deactivation by haloperidol. c. Basal BRET ratios calculated before the application of dopamine that reflect the extent of the Gαolf-Gβγ heterotrimer formation. d. Changes in the BRET ratio from basal signal to maximal response that reflect the amplitude of the response. e. Analysis of the expression levels of Gαolf and Gβγ (detected by anti-GFP antibodies) subunits by Western blotting. Ponceau S staining of total cell lysates was used as a loading control. Results represent the mean of quadruplicate wells from a typical experiment. Similar results were seen in two independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. One way ANOVA followed by the Holm–Sidak method were performed to determine statistically significant differences. Asterisks indicate statistical significance from wild type control: ***, p < 0.001. The Gαolf vectors were based on transcript NM_001142339.